Determination of Isoflavones in Radix puerariae from Different Origins by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Based on Optimal Pretreatment Method
- PMID: 36832868
- PMCID: PMC9955973
- DOI: 10.3390/foods12040794
Determination of Isoflavones in Radix puerariae from Different Origins by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Based on Optimal Pretreatment Method
Abstract
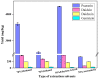
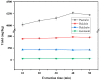
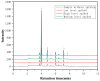
A new method for simultaneous determination of puerarin, daidzin, daidzein and genistein in Radix puerariae by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography was established. The target analytes were extracted from Radix puerariae by 70% ethylene glycol with the assistance of ultrasonication, purified by the absorption of N-propyl ethylenediamine (PSA), and separated on a Supersil ODS column (4.6 mm × 250 mm × 2.5 μm). Gradient elution in 12 min was performed with the mobile phase 0.1% formic acid(A)-acetonitrile(B). The column temperature was 25 °C and the flow rate was 1 mL/min. The detection wavelength of the four target analytes was 250 nm. The limits of detection (LODs) of puerarin, daidzin, daidzein and genistein were 0.086 mg/L, 0.020 mg/L, 0.027 mg/L and 0.037 mg/L, respectively, and limits of quantitation (LOQs) were 0.29 mg/L, 0.065 mg/L, 0.090 mg/L and 0.12 mg/L, respectively. The recovery of the four substances ranged from 90.5% to 109.6%, and the relative standard deviation (n = 6) was less than 7.7%. With the established methods, puerarin, daidzin, daidzein and genistein in Radix puerariae from 11 origins were determined. The contents of the four compounds varied with the origin and variety. It provides basic data and technical means for quality control and regulation of Radix puerariae.
Keywords: Radix puerariae; dispersed solid phase purification; isoflavones; ultra-high performance liquid chromatography.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[A simultaneous determination of daidzin and puerarin and determination of daidzein in Oriental pharmaceutical decoctions containing puerariae radix by ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography].Yakugaku Zasshi. 1993 Dec;113(12):881-9. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.113.12_881. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1993. PMID: 8301541 Japanese.
-
LC-MS/MS determination and pharmacokinetics study of puerarin and daidzein in rat plasma after oral administration of Gegenqinlian decoction and Radix Puerariae extract.Pharmacogn Mag. 2014 Jul;10(39):241-8. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.137363. Pharmacogn Mag. 2014. PMID: 25210310 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous analysis and retention behavior of major isoflavonoids in Radix Puerariae lobatae and Radix Puerariae thomsonii by high performance liquid chromatography with cyclodextrins as a mobile phase modifier.Anal Chim Acta. 2012 Jan 27;712:145-51. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2011.10.061. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Anal Chim Acta. 2012. PMID: 22177078
-
Evaluation of quality of Radix Puerariae herbal medicine by isoflavonoids.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010 May;62(5):644-50. doi: 10.1211/jpp.62.05.0013. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20609068
-
Constituent isoflavones of Puerariae radix as a potential neuroprotector in cognitive impairment: Evidence from preclinical studies.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Sep;90:102040. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.102040. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 37619620 Review.
References
-
- Zhu Y., Wang B., Ma M. Pathogenesis of acute hemolysis and renal failure induced by puerarin. Chin. J. New Med. Clin. Med. 2003;22:699–702.
-
- Guan L., Chen Z. Possible developmental and reproductive toxicity of isoflavones in soybean and Kudzu root. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005;14:S105.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

