Effect of an Integrated Physiotherapy Protocol on Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A Preliminary Study
- PMID: 36833098
- PMCID: PMC9956031
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare11040564
Effect of an Integrated Physiotherapy Protocol on Knee Osteoarthritis Patients: A Preliminary Study
Abstract
Background: Exercise therapy can potentially relieve symptoms and improve functional status of the knee osteoarthritis population. Despite the proved practical benefits, there is no standard, comprehensive physiotherapeutic protocol available targeting the physical and physiological impairment cluster associated with disease. Osteoarthritis is a whole joint disease, affecting joint cartilage, ligaments, menisci and joint associated muscles, from variable pathophysiological processes. Hence, there is a need to develop a physiotherapy protocol to address the multi-structural physical, physiological and functional impairments associated with the disease.
Objective: The objective of the present study is to evaluate the efficacy of designed, therapist supervised, patient education, progressive resistance exercises, passive stretching exercises, soft tissue manipulation, muscle energy technique, Maitland mobilization, aerobic exercise, and neuromuscular training physiotherapy protocol on pain, disability, balance, and physical functional performance in knee osteoarthritis patients.
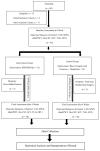
Methodology: The preliminary study was conducted on a (n = 60) sample of convenience. The samples were randomly allocated into two study groups, intervention, and control group. The control group was advised on a basic home program. On the other hand, the treatment of the intervention group was designed with a therapist supervised Physiotherapy Protocol. The outcome variables studied were the Visual Analogue Scale, Modified WOMAC Scale, Timed Up and Go Test, Functional Reach Test, 40 m Fast Paced Walk Test, Stair Climb Test, 30 s Chair Stand Test.
Results: The results of the study revealed a significant improvement among most of the studied outcome measures in the intervention group, hence the designed supervised physiotherapy protocol was found effective in relieving multiple physiological impairments associated with this whole joint disease.
Keywords: balance; disability; exercise therapy; functional performance; knee osteoarthritis; manual therapy; pain; physiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Murray C.J., Vos T., Lozano R., Naghavi M., Flaxman A.D., Michaud C., Ezzati M., Shibuya K., Salomon J.A., Abdalla S., et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2197–2223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vos T., Flaxman A.D., Naghavi M., Lozano R., Michaud C., Ezzati M., Shibuya K., Salomon J.A., Abdalla S., Aboyans V., et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2163–2196. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61729-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Briggs A.M., Cross M.J., Hoy D.G., Sanchez-Riera L., Blyth F.M., Woolf A.D., March L. Musculoskeletal health conditions represent a global threat to healthy aging: A report for the 2015 World Health Organization world report on ageing and health. Gerontologist. 2016;56((Suppl. 2)):S243–S255. doi: 10.1093/geront/gnw002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kaur R., Sharma V.L., Singh A. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis and its correlation in women of rural and urban parts of Hoshiarpur (Punjab) J. Postgrad. Med. Educ. Res. 2015;49:32. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10028-1139. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

