Progress in and Prospects of Genome Editing Tools for Human Disease Model Development and Therapeutic Applications
- PMID: 36833410
- PMCID: PMC9957140
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14020483
Progress in and Prospects of Genome Editing Tools for Human Disease Model Development and Therapeutic Applications
Abstract
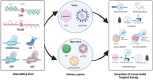
Programmable nucleases, such as zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs), transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs), and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/Cas, are widely accepted because of their diversity and enormous potential for targeted genomic modifications in eukaryotes and other animals. Moreover, rapid advances in genome editing tools have accelerated the ability to produce various genetically modified animal models for studying human diseases. Given the advances in gene editing tools, these animal models are gradually evolving toward mimicking human diseases through the introduction of human pathogenic mutations in their genome rather than the conventional gene knockout. In the present review, we summarize the current progress in and discuss the prospects for developing mouse models of human diseases and their therapeutic applications based on advances in the study of programmable nucleases.
Keywords: genome editing; mouse model of human disease; programmable nuclease; therapeutic application.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Applications of Alternative Nucleases in the Age of CRISPR/Cas9.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 29;18(12):2565. doi: 10.3390/ijms18122565. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29186020 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Basics of genome editing technology and its application in livestock species.Reprod Domest Anim. 2017 Aug;52 Suppl 3:4-13. doi: 10.1111/rda.13012. Reprod Domest Anim. 2017. PMID: 28815851 Review.
-
Construction and Evaluation of Zinc Finger Nucleases.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2637:1-25. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3016-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36773134
-
Concerns regarding 'off-target' activity of genome editing endonucleases.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018 Oct;131:22-30. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2018.03.027. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29653762 Review.
-
Applications of genome editing technology in the targeted therapy of human diseases: mechanisms, advances and prospects.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jan 3;5(1):1. doi: 10.1038/s41392-019-0089-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32296011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of Gene Editing and Nanotechnology in Stem Cell-Based Therapies for Human Diseases.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025 May;21(4):905-934. doi: 10.1007/s12015-025-10857-0. Epub 2025 Feb 27. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2025. PMID: 40014250 Review.
-
Liver-specific transgenic expression of human NTCP in rhesus macaques confers HBV susceptibility on primary hepatocytes.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Feb 18;122(7):e2413771122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2413771122. Epub 2025 Feb 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39937851 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

