The Role of Web-Based Adaptive Choice-Based Conjoint Analysis Technology in Eliciting Patients' Preferences for Osteoarthritis Treatment
- PMID: 36834057
- PMCID: PMC9959784
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20043364
The Role of Web-Based Adaptive Choice-Based Conjoint Analysis Technology in Eliciting Patients' Preferences for Osteoarthritis Treatment
Abstract
Objective: To assess the feasibility of using adaptive choice-based conjoint (ACBC) analysis to elicit patients' preferences for pharmacological treatment of osteoarthritis (OA), patients' satisfaction with completing the ACBC questionnaire, and factors associated with questionnaire completion time.
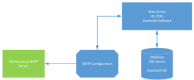
Methods: Adult patients aged 18 years and older with a medical diagnosis of OA, experiencing joint pain in the past 12 months, and living in the Northeast of England participated in the study. The participants completed a web-based ACBC questionnaire about their preferences regarding pharmaceutical treatment for OA using a touchscreen laptop independently, and accordingly, the questionnaire completion time was measured. Moreover, the participants completed a pen-and-paper feedback form about their experience in completing the ACBC questionnaire.
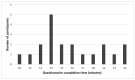
Results: Twenty participants aged 40 years and older, 65% females, 75% had knee OA, and suffering from OA for more than 5 years participated in the study. About 60% of participants reported completing a computerized questionnaire in the past. About 85% of participants believed that the ACBC task helped them in making decisions regarding their OA medications, and 95% agreed or strongly agreed that they would be happy to complete a similar ACBC questionnaire in the future. The average questionnaire completion time was 16 min (range 10-24 min). The main factors associated with longer questionnaire completion time were older age, never using a computer in the past, and no previous experience in completing a questionnaire.
Conclusions: The ACBC analysis is a feasible and efficient method to elicit patients' preferences for pharmacological treatment of OA, which could be used in clinical settings to facilitate shared decision-making and patient-centered care. The ACBC questionnaire completion consumes a significantly longer time for elderly participants, who never used a computer, and never completed any questionnaire previously. Therefore, the contribution of patients and public involvement (PPI) group in the development of the ACBC questionnaire could facilitate participants' understanding and satisfaction with the task. Future research including patients with different chronic conditions may provide more useful information about the efficiency of ACBC analysis in eliciting patients' preferences for osteoarthritis treatment.
Keywords: adaptive choice-based conjoint; conjoint analysis; osteoarthritis; patients’ preferences; shared decision making; web-based.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- NICE Overview|Osteoarthritis: Care and Management|Guidance|NICE. [(accessed on 7 November 2020)]. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg177.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

