The Cost-Effectiveness of Homecare Services for Adults and Older Adults: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36834068
- PMCID: PMC9960182
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20043373
The Cost-Effectiveness of Homecare Services for Adults and Older Adults: A Systematic Review
Abstract
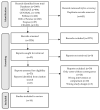
This study provides an overview of the literature on the cost-effectiveness of homecare services compared to in-hospital care for adults and older adults. A systematic review was performed using Medline, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, CINAHL and CENTRAL databases from inception to April 2022. The inclusion criteria were as follows: (i) (older) adults; (ii) homecare as an intervention; (iii) hospital care as a comparison; (iv) a full economic evaluation examining both costs and consequences; and (v) economic evaluations arising from randomized controlled trials (RCTs). Two independent reviewers selected the studies, extracted data and assessed study quality. Of the 14 studies identified, homecare, when compared to hospital care, was cost-saving in seven studies, cost-effective in two and more effective in one. The evidence suggests that homecare interventions are likely to be cost-saving and as effective as hospital. However, the included studies differ regarding the methods used, the types of costs and the patient populations of interest. In addition, methodological limitations were identified in some studies. Definitive conclusions are limited and highlight the need for better standardization of economic evaluations in this area. Further economic evaluations arising from well-designed RCTs would allow healthcare decision-makers to feel more confident in considering homecare interventions.
Keywords: adults; economic evaluation; homecare; hospital care; older adults.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Fact sheet. 2022. [(accessed on 20 July 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health.
-
- Rajao F.L., Martins M. Home Care in Brazil: An exploratory study on the construction process and service use in the Brazilian Health System. Cien Saude Colet. 2020;25:1863–1877. - PubMed
-
- Mendes E.V. As Redes de Atenção à Saúde [The Healthcare Networks] Organização Pan-Americana da Saúde; Brasília, Brazil: 2011. 549p
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous