Seroprevalence of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Following the Omicron BA.1 Wave
- PMID: 36834360
- PMCID: PMC9959557
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph20043665
Seroprevalence of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies Following the Omicron BA.1 Wave
Abstract
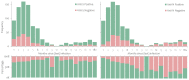
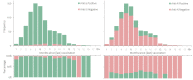
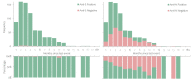
We conducted a seroprevalence study using convenient residual sera samples from the Slovenian population collected after the end of the Omicron BA.1 pandemic wave. Serum samples were tested for spike glycoprotein (anti-S) and nucleocapsid protein (anti-N) antibodies. Participants' data regarding confirmed infection and vaccination was obtained from national registries. Anti-S antibodies were detected in 2439 (84.1%) of 2899 sera from persons aged 0-90 years, with the lowest prevalence in the 0-17 age group. The proportion of anti-N positives was the lowest in the ≥70 age group. The proportion of anti-N positives was significantly higher among participants with confirmed past infection and among those who had never been vaccinated. In participants who had not been notified as infected and who had never been vaccinated, the seroprevalence of anti-S and anti-N antibodies was 53% and 35.5%, respectively. From the time of serum collection to mid-November 2022, 445 participants (15.3%) tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, with higher odds in seronegative participants, participants in the 40-59 age group, and those without notified previous infection. Vaccination status and gender had no significant effects on infection risk. This study underlines the importance of serosurveys in understanding the development of the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; Omicron BA.1; anti-nucleocapsid protein antibodies; anti-spike glycoprotein antibodies; seroprevalence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Röltgen K., Powell A.E., Wirz O.F., Stevens B.A., Hogan C.A., Najeeb J., Hunter M., Wang H., Sahoo M.K., Huang C., et al. Defining the Features and Duration of Antibody Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Infection Associated with Disease Severity and Outcome. Sci. Immunol. 2020;5:eabe0240. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe0240. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

