Identify the Virus-like Models for COVID-19 as Bio-Threats: Combining Phage Display, Spectral Detection and Algorithms Analysis
- PMID: 36834622
- PMCID: PMC9967019
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043209
Identify the Virus-like Models for COVID-19 as Bio-Threats: Combining Phage Display, Spectral Detection and Algorithms Analysis
Abstract
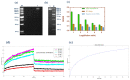
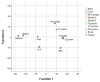
The rapid identification and recognition of COVID-19 have been challenging since its outbreak. Multiple methods were developed to realize fast monitoring early to prevent and control the pandemic. In addition, it is difficult and unrealistic to apply the actual virus to study and research because of the highly infectious and pathogenic SARS-CoV-2. In this study, the virus-like models were designed and produced to replace the original virus as bio-threats. Three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence and Raman spectroscopy were employed for differentiation and recognition among the produced bio-threats and other viruses, proteins, and bacteria. Combined with PCA and LDA analysis, the identification of the models for SARS-CoV-2 was achieved, reaching a correction of 88.9% and 96.3% after cross-validation, respectively. This idea might provide a possible pattern for detecting and controlling SARS-CoV-2 from the perspective of combining optics and algorithms, which could be applied in the early-warning system against COVID-19 or other bio-threats in the future.
Keywords: PCA-LDA; SARS-CoV-2; identification; phage display; spectroscopy; virus-like models.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Construction, Characterization, and Application of a Nonpathogenic Virus-like Model for SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein by Phage Display.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Oct 4;14(10):683. doi: 10.3390/toxins14100683. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36287952 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Phage Display Technology for Sensor-Based Virus Detection: Current Status and Future Prospects.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Jun 9;13(6):640. doi: 10.3390/bios13060640. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37367005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive characterization of the antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein finds additional vaccine-induced epitopes beyond those for mild infection.Elife. 2022 Jan 24;11:e73490. doi: 10.7554/eLife.73490. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35072628 Free PMC article.
-
Early warning and rapid public health response to prevent COVID-19 outbreaks in long-term care facilities (LTCF) by monitoring SARS-CoV-2 RNA in LTCF site-specific sewage samples and assessment of antibodies response in this population: prospective study protocol.BMJ Open. 2021 Aug 20;11(8):e052282. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052282. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 34417219 Free PMC article.
-
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy as a Potential COVID-19 Early Detection Method: A Review and Future Perspective.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 10;22(12):4391. doi: 10.3390/s22124391. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35746172 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

