Circular RNAs and Untranslated Regions in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- PMID: 36834627
- PMCID: PMC9967498
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043215
Circular RNAs and Untranslated Regions in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
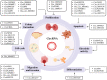
Before the advent of next-generation sequencing, research on acute myeloid leukemia (AML) mostly centered on protein-coding genes. In recent years, breakthroughs in RNA sequencing technologies and whole transcriptome analysis have led to the discovery that approximately 97.5% of the human genome is transcribed into non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). This paradigm shift has led to an explosion of research interest in different classes of non-coding RNAs, such as circular RNAs (circRNAs) as well as non-coding untranslated regions (UTRs) of protein-coding messenger RNAs. The critical roles of circRNAs and UTRs in AML pathogenesis have become increasingly apparent. In this review, we discuss the cellular mechanisms of circRNAs and summarize recent studies that reveal their biological roles in AML. Furthermore, we also review the contribution of 3'UTRs to disease progression. Finally, we discuss the potential of circRNAs and 3'UTRs as new biomarkers for disease stratification and/or the prediction of treatment response and targets for the development of RNA-directed therapeutic applications.
Keywords: 3′UTR splicing; 3′untranslated region; alternative polyadenylation; circular RNA; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Dohner H., Wei A.H., Appelbaum F.R., Craddock C., DiNardo C.D., Dombret H., Ebert B.L., Fenaux P., Godley L.A., Hasserjian R.P., et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood. 2022;140:1345–1377. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022016867. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Megias-Vericat J.E., Rojas L., Herrero M.J., Boso V., Montesinos P., Moscardo F., Poveda J.L., Sanz M.A., Alino S.F. Influence of ABCB1 polymorphisms upon the effectiveness of standard treatment for acute myeloid leukemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Pharm. J. 2015;15:109–118. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2014.80. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

