Staphylococcus aureus Genomic Analysis and Outcomes in Patients with Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36834650
- PMCID: PMC9967247
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043234
Staphylococcus aureus Genomic Analysis and Outcomes in Patients with Bone and Joint Infections: A Systematic Review
Abstract
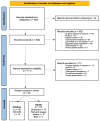
Many studies have been published assessing the association between the presence of S. aureus genes and outcomes in patients with bone and joint infections (BJI), but it is not known if they have had similar findings. A systematic literature review was performed. All available data on studies in Pubmed between January 2000 to October 2022 reporting the genetic characteristics of S. aureus and the outcomes of BJIs were analyzed. BJI included prosthetic joint infection (PJI), osteomyelitis (OM), diabetic foot infection (DFI), and septic arthritis. Because of the heterogeneity of studies and outcomes, no meta-analysis was performed. With the search strategy, 34 articles were included: 15 articles on children and 19 articles on adults. In children, most BJI studied were OM (n = 13) and septic arthritis (n = 9). Panton Valentine leucocidin (PVL) genes were associated with higher biological inflammatory markers at presentation (n = 4 studies), more febrile days (n = 3), and more complicated/severe infection (n = 4). Other genes were reported anecdotally associated with poor outcomes. In adults, six studies reported outcomes in patients with PJI, 2 with DFI, 3 with OM, and 3 with various BJI. Several genes were associated with a variety of poor outcomes in adults, but studies found contradictory results. Whereas PVL genes were associated with poor outcomes in children, no specific genes were reported similarly in adults. Additional studies with homogenous BJI and larger sample sizes are needed.
Keywords: Panton Valentine leucocidin; Staphylococcus aureus; agr; bone and joint infections; osteomyelitis; outcome; prosthetic joint infection; septic arthritis; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Case report: Personalized triple phage-antibiotic combination therapy to rescue necrotizing fasciitis caused by Panton-Valentine leukocidin-producing MRSA in a 12-year-old boy.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 17;14:1354681. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1354681. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39355265 Free PMC article.
-
Hyaluronic Acid-Based Microparticles with Lubrication and Anti-Inflammation for Alleviating Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis.Biomater Res. 2024 Sep 6;28:0073. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0073. eCollection 2024. Biomater Res. 2024. PMID: 39247653 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Microbial Landscape of Bone and Joint Infections: An Analysis Using 16S rRNA Metagenome Sequencing.Infect Drug Resist. 2024 Dec 13;17:5557-5566. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S482931. eCollection 2024. Infect Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39691489 Free PMC article.
-
The role of FTO in m6A RNA methylation and immune regulation in Staphylococcus aureus infection-related osteomyelitis.Front Microbiol. 2025 Feb 6;16:1526475. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1526475. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 39980685 Free PMC article.
-
Resistance Genes and Virulence Factor Genes in Coagulase-Negative and Positive Staphylococci of the Staphylococcus intermedius Group (SIG) Isolated from the Dog Skin.Microorganisms. 2025 Mar 25;13(4):735. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040735. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Souli M., Ruffin F., Choi S.-H., Park L.P., Gao S., Lent N.C., Sharma-Kuinkel B.K., Thaden J.T., Maskarinec S.A., Wanda L., et al. Changing Characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia: Results From a 21-Year, Prospective, Longitudinal Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019;69:1868–1877. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical