Acute PDE4 Inhibition Induces a Transient Increase in Blood Glucose in Mice
- PMID: 36834669
- PMCID: PMC9963939
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043260
Acute PDE4 Inhibition Induces a Transient Increase in Blood Glucose in Mice
Abstract
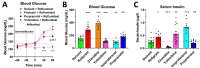
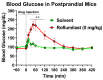
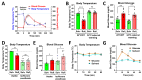
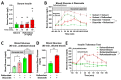
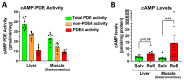
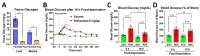
cAMP-phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitors are currently approved for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. There is interest in expanding the therapeutic application of PDE4 inhibitors to metabolic disorders, as their chronic application induces weight loss in patients and animals and improves glucose handling in mouse models of obesity and diabetes. Unexpectedly, we have found that acute PDE4 inhibitor treatment induces a temporary increase, rather than a decrease, in blood glucose levels in mice. Blood glucose levels in postprandial mice increase rapidly upon drug injection, reaching a maximum after ~45 min, and returning to baseline within ~4 h. This transient blood glucose spike is replicated by several structurally distinct PDE4 inhibitors, suggesting that it is a class effect of PDE4 inhibitors. PDE4 inhibitor treatment does not reduce serum insulin levels, and the subsequent injection of insulin potently reduces PDE4 inhibitor-induced blood glucose levels, suggesting that the glycemic effects of PDE4 inhibition are independent of changes in insulin secretion and/or sensitivity. Conversely, PDE4 inhibitors induce a rapid reduction in skeletal muscle glycogen levels and potently inhibit the uptake of 2-deoxyglucose into muscle tissues. This suggests that reduced glucose uptake into muscle tissue is a significant contributor to the transient glycemic effects of PDE4 inhibitors in mice.
Keywords: 2-deoxyglucose; PDE4; adrenergic signaling; blood glucose; cAMP-phosphodiesterase; insulin; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
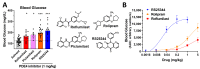

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of type 4 cAMP-phosphodiesterases (PDE4s) in mice induces hypothermia via effects on behavioral and central autonomous thermoregulation.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Oct;180:114158. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2020.114158. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32702371 Free PMC article.
-
Roflumilast-Mediated Phosphodiesterase 4D Inhibition Reverses Diabetes-Associated Cardiac Dysfunction and Remodeling: Effects Beyond Glucose Lowering.Diabetes. 2022 Aug 1;71(8):1660-1678. doi: 10.2337/db21-0898. Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 35594380
-
PAN-selective inhibition of cAMP-phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) induces gastroparesis in mice.FASEB J. 2020 Sep;34(9):12533-12548. doi: 10.1096/fj.202001016RR. Epub 2020 Aug 1. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32738081 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors in diabetic nephropathy.Cell Signal. 2022 Feb;90:110185. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110185. Epub 2021 Nov 14. Cell Signal. 2022. PMID: 34785349 Review.
-
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) and neurological disorders: A promising frontier in neuropharmacology.Adv Pharmacol. 2025;102:159-209. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2024.10.005. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Adv Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39929579 Review.
Cited by
-
The flavonoid Sudachitin regulates glucose metabolism via PDE inhibition.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 8;10(16):e35978. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35978. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39224336 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

