Specific Activation of Yamanaka Factors via HSF1 Signaling in the Early Stage of Zebrafish Optic Nerve Regeneration
- PMID: 36834675
- PMCID: PMC9961437
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043253
Specific Activation of Yamanaka Factors via HSF1 Signaling in the Early Stage of Zebrafish Optic Nerve Regeneration
Abstract
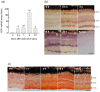
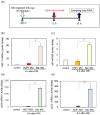
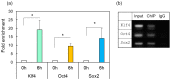
In contrast to the case in mammals, the fish optic nerve can spontaneously regenerate and visual function can be fully restored 3-4 months after optic nerve injury (ONI). However, the regenerative mechanism behind this has remained unknown. This long process is reminiscent of the normal development of the visual system from immature neural cells to mature neurons. Here, we focused on the expression of three Yamanaka factors (Oct4, Sox2, and Klf4: OSK), which are well-known inducers of induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells in the zebrafish retina after ONI. mRNA expression of OSK was rapidly induced in the retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) 1-3 h after ONI. Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) mRNA was most rapidly induced in the RGCs at 0.5 h. The activation of OSK mRNA was completely suppressed by the intraocular injection of HSF1 morpholino prior to ONI. Furthermore, the chromatin immunoprecipitation assay showed the enrichment of OSK genomic DNA bound to HSF1. The present study clearly showed that the rapid activation of Yamanaka factors in the zebrafish retina was regulated by HSF1, and this sequential activation of HSF1 and OSK might provide a key to unlocking the regenerative mechanism of injured RGCs in fish.
Keywords: HSF1; Klf4; Oct4; Sox2; Yamanaka factors; optic nerve regeneration; retina; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transglutaminase 2 Regulates HSF1 Gene Expression in the Acute Phase of Fish Optic Nerve Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 21;25(16):9078. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169078. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201764 Free PMC article.
-
HSP70, the earliest-induced gene in the zebrafish retina during optic nerve regeneration: its role in cell survival.Neurochem Int. 2011 Jul;58(8):888-95. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2011.02.017. Epub 2011 Feb 19. Neurochem Int. 2011. PMID: 21338645
-
A novel activation mechanism of cellular Factor XIII in zebrafish retina after optic nerve injury.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019 Sep 10;517(1):57-62. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.003. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019. PMID: 31296382
-
A molecular mechanism of optic nerve regeneration in fish: the retinoid signaling pathway.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013 Nov;37:13-30. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2013.07.004. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2013. PMID: 23994437 Review.
-
[Inhibition of stress-responsive signaling pathway prevents neural cell death following optic nerve injury].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2014 Nov;118(11):907-15. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 25543382 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Rapid Activation of MYDGF Is Critical for Cell Survival in the Acute Phase of Retinal Regeneration in Fish.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 27;26(15):7251. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157251. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806387 Free PMC article.
-
Transglutaminase 2 Regulates HSF1 Gene Expression in the Acute Phase of Fish Optic Nerve Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 21;25(16):9078. doi: 10.3390/ijms25169078. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201764 Free PMC article.
-
Optic Neuropathies: Current and Future Strategies for Optic Nerve Protection and Repair.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 10;24(8):6977. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086977. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108140 Free PMC article.
-
Adult Neurogenesis of Teleost Fish Determines High Neuronal Plasticity and Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 25;25(7):3658. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073658. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

