Cholesterol-Lowering Activity of Vitisin A Is Mediated by Inhibiting Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Enhancing LDL Uptake in HepG2 Cells
- PMID: 36834719
- PMCID: PMC9961218
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043301
Cholesterol-Lowering Activity of Vitisin A Is Mediated by Inhibiting Cholesterol Biosynthesis and Enhancing LDL Uptake in HepG2 Cells
Abstract
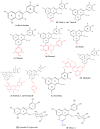
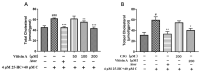
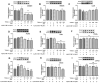
Pyranoanthocyanins have been reported to possess better chemical stability and bioactivities than monomeric anthocyanins in some aspects. The hypocholesterolemic activity of pyranoanthocyanins is unclear. In view of this, this study was conducted to compare the cholesterol-lowering activities of Vitisin A with the anthocyanin counterpart Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside(C3G) in HepG2 cells and to investigate the interaction of Vitisin A with the expression of genes and proteins associated with cholesterol metabolism. HepG2 cells were incubated with 40 μM cholesterol and 4 μM 25-hydroxycholeterol with various concentrations of Vitisin A or C3G for 24 h. It was found that Vitisin A decreased the cholesterol levels at the concentrations of 100 μM and 200 μM with a dose-response relationship, while C3G exhibited no significant effect on cellular cholesterol. Furthermore, Vitisin A could down-regulate 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl coenzyme A reductase (HMGCR) to inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis through a sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2)-dependent mechanism, and up-regulate low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) and blunt the secretion of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) protein to promote intracellular LDL uptake without LDLR degradation. In conclusion, Vitisin A demonstrated hypocholesterolemic activity, by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis and enhancing LDL uptake in HepG2 cells.
Keywords: HMGCR; LDL uptake; Vitisin A; cholesterol biosynthesis; pyranoanthocyanins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of neolignans with PCSK9 downregulatory and LDLR upregulatory activities from Penthorum chinense and the potential in cholesterol uptake by transcriptional regulation of LDLR via SREBP2.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 5;278:114265. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114265. Epub 2021 Jun 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34111537
-
Deferoxamine stimulates LDLR expression and LDL uptake in HepG2 cells.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016 Mar;60(3):600-8. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500467. Epub 2015 Dec 9. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2016. PMID: 26577249
-
The Cholesterol-Modulating Effect of Methanol Extract of Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.) Leaves on Regulating LDLR and PCSK9 Expression in HepG2 Cells.Molecules. 2019 Jan 30;24(3):493. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030493. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30704067 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 for the treatment of dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;62(16):1401-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.07.056. Epub 2013 Aug 21. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23973703 Review.
-
Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin-Type 9 and Lipid Metabolism.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1276:137-156. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-6082-8_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32705598 Review.
Cited by
-
Theabrownin from Dark Tea Ameliorates Insulin Resistance via Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Modulating IRS-1/PI3K/Akt Pathway in HepG2 Cells.Nutrients. 2023 Sep 5;15(18):3862. doi: 10.3390/nu15183862. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37764646 Free PMC article.
-
Vitisin A Outperforms Cyanidin-3-O-Glucoside in Triglyceride Reduction by Modulating Hepatic Lipogenesis and Fatty Acid β-Oxidation.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Feb 11;26(4):1521. doi: 10.3390/ijms26041521. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40003987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhong V.W., Van Horn L., Cornelis M.C., Wilkins J.T., Ning H., Carnethon M.R., Greenland P., Mentz R.J., Tucker K.L., Zhao L., et al. Associations of Dietary Cholesterol or Egg Consumption With Incident Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality. JAMA. 2019;321:1081–1095. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.1572. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

