Therapeutic Effect of Curcumin on Metabolic Diseases: Evidence from Clinical Studies
- PMID: 36834734
- PMCID: PMC9959718
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043323
Therapeutic Effect of Curcumin on Metabolic Diseases: Evidence from Clinical Studies
Abstract
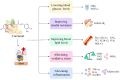
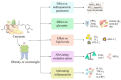
Metabolic diseases have become a serious threat to human health worldwide. It is crucial to look for effective drugs from natural products to treat metabolic diseases. Curcumin, a natural polyphenolic compound, is mainly obtained from the rhizomes of the genus Curcuma. In recent years, clinical trials using curcumin for the treatment of metabolic diseases have been increasing. In this review, we provide a timely and comprehensive summary of the clinical progress of curcumin in the treatment of three metabolic diseases, namely type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The therapeutic effects and underlying mechanisms of curcumin on these three diseases are presented categorically. Accumulating clinical evidence demonstrates that curcumin has good therapeutic potential and a low number of side effects for the three metabolic diseases. It can lower blood glucose and lipid levels, improve insulin resistance and reduce inflammation and oxidative stress. Overall, curcumin may be an effective drug for the treatment of T2DM, obesity and NAFLD. However, more high-quality clinical trials are still required in the future to verify its efficacy and determine its molecular mechanisms and targets.
Keywords: clinical evidence; curcumin; diabetes; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Sun H., Saeedi P., Karuranga S., Pinkepank M., Ogurtsova K., Duncan B.B., Stein C., Basit A., Chan J.C.N., Mbanya J.C., et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022;183:109119. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williamson R.M., Price J.F., Glancy S., Perry E., Nee L.D., Hayes P.C., Frier B.M., Van Look L.A., Johnston G.I., Reynolds R.M., et al. Prevalence of and risk factors for hepatic steatosis and nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease in people with type 2 diabetes: The Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care. 2011;34:1139–1144. doi: 10.2337/dc10-2229. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

