Hormonal Gut-Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
- PMID: 36834794
- PMCID: PMC9959457
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043384
Hormonal Gut-Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Abstract
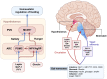
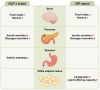
The brain, particularly the hypothalamus and brainstem, monitors and integrates circulating metabolic signals, including gut hormones. Gut-brain communication is also mediated by the vagus nerve, which transmits various gut-derived signals. Recent advances in our understanding of molecular gut-brain communication promote the development of next-generation anti-obesity medications that can safely achieve substantial and lasting weight loss comparable to metabolic surgery. Herein, we comprehensively review the current knowledge about the central regulation of energy homeostasis, gut hormones involved in the regulation of food intake, and clinical data on how these hormones have been applied to the development of anti-obesity drugs. Insight into and understanding of the gut-brain axis may provide new therapeutic perspectives for the treatment of obesity and diabetes.
Keywords: anti-obesity agents; brainstem; energy metabolism; gut hormones; hypothalamus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kim C.S., Ko S.H., Kwon H.S., Kim N.H., Kim J.H., Lim S., Choi S.H., Song K.H., Won J.C., Kim D.J., et al. Prevalence, awareness, and management of obesity in Korea: Data from the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey (1998–2011) Diabetes Metab. J. 2014;38:35–43. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.35. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chin S.O., Hwang Y.C., Ahn H.Y., Jun J.E., Jeong I.K., Ahn K.J., Chung H.Y. Trends in the Prevalence of Obesity and Its Phenotypes Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2007 to 2017 in Korea. Diabetes Metab. J. 2022;46:808–812. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2021.0226. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

