Tyk2 Targeting in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 36834806
- PMCID: PMC9959504
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043391
Tyk2 Targeting in Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
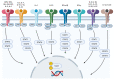
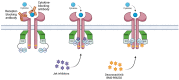
The Janus kinase (Jak)/signal transducer and activating protein (STAT) pathways mediate the intracellular signaling of cytokines in a wide spectrum of cellular processes. They participate in physiologic and inflammatory cascades and have become a major focus of research, yielding novel therapies for immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMID). Genetic linkage has related dysfunction of Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2)-the first member of the Jak family that was described-to protection from psoriasis. Furthermore, Tyk2 dysfunction has been related to IMID prevention, without increasing the risk of serious infections; thus, Tyk2 inhibition has been established as a promising therapeutic target, with multiple Tyk2 inhibitors under development. Most of them are orthosteric inhibitors, impeding adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding to the JH1 catalytic domain-which is highly conserved across tyrosine kinases-and are not completely selective. Deucravacitinib is an allosteric inhibitor that binds to the pseudokinase JH2 (regulatory) domain of Tyk2; this unique mechanism determines greater selectivity and a reduced risk of adverse events. In September 2022, deucravacitinib became the first Tyk2 inhibitor approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe psoriasis. A bright future can be expected for Tyk2 inhibitors, with newer drugs and more indications to come.
Keywords: inflammatory diseases; psoriasis; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
L. Rusiñol declares no conflicts of interest for the related topic. L. Puig has received consultancy/speaker’s honoraria from and/or participated in clinical trials sponsored by Abbvie, Almirall, Amgen, Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb, Boehringer Ingelheim, Celgene, Fresenius-Kabi, Gebro, Janssen, JS BIOCAD, Leo-Pharma, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung-Bioepis, and UCB.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

