Novel Therapeutic Potential of Retinoid-Related Orphan Receptor α in Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 36834872
- PMCID: PMC9959049
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043462
Novel Therapeutic Potential of Retinoid-Related Orphan Receptor α in Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
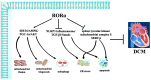
The retinoid-related orphan receptor α (RORα) is one subfamily of nuclear hormone receptors (NRs). This review summarizes the understanding and potential effects of RORα in the cardiovascular system and then analyzes current advances, limitations and challenges, and further strategy for RORα-related drugs in cardiovascular diseases. Besides regulating circadian rhythm, RORα also influences a wide range of physiological and pathological processes in the cardiovascular system, including atherosclerosis, hypoxia or ischemia, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury, diabetic cardiomyopathy, hypertension, and myocardial hypertrophy. In terms of mechanism, RORα was involved in the regulation of inflammation, apoptosis, autophagy, oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and mitochondrial function. Besides natural ligands for RORα, several synthetic RORα agonists or antagonists have been developed. This review mainly summarizes protective roles and possible mechanisms of RORα against cardiovascular diseases. However, there are also several limitations and challenges of current research on RORα, especially the difficulties on the transformability from the bench to the bedside. By the aid of multidisciplinary research, breakthrough progress on RORα-related drugs to combat cardiovascular disorder may appear.
Keywords: agonist; cardiovascular diseases; ligand; retinoid-related orphan receptor α; staggerer mutant mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Han D., Wang Y., Chen J., Zhang J., Yu P., Zhang R., Li S., Tao B., Wang Y., Qiu Y., et al. Activation of melatonin receptor 2 but not melatonin receptor 1 mediates melatonin-conferred cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Pineal Res. 2019;67:e12571. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12571. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Xu L., Su Y., Zhao Y., Sheng X., Tong R., Ying X., Gao L., Ji Q., Gao Y., Yan Y., et al. Melatonin differentially regulates pathological and physiological cardiac hypertrophy: Crucial role of circadian nuclear receptor RORalpha signaling. J. Pineal Res. 2019;67:e12579. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12579. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82270418, 82070280, 82200313, 81770266/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022-3-16-670/the "333 Project" of Jiangsu Province
- 21KJB310014/Natural Science Research in Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions
- 2018-WSN-062/Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province
- MS22020006/Natural Science Foundations of Nantong City
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

