Ejaculatory Abstinence Affects the Sperm Quality in Normozoospermic Men-How Does the Seminal Bacteriome Respond?
- PMID: 36834909
- PMCID: PMC9963725
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043503
Ejaculatory Abstinence Affects the Sperm Quality in Normozoospermic Men-How Does the Seminal Bacteriome Respond?
Abstract
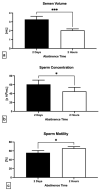
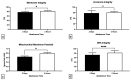
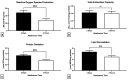
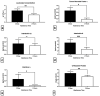
This study was designed to describe bacterial profiles of ejaculates collected following a long and short ejaculatory abstinence set in the context of changes in the conventional, oxidative, and immunological characteristics of semen. Two specimens were collected in succession from normozoospermic men (n = 51) following 2 days and 2 h, respectively. Semen samples were processed and analyzed according to the World Health Organization (WHO) 2021 guidelines. Afterwards, sperm DNA fragmentation, mitochondrial function, levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS), total antioxidant capacity, and oxidative damage to sperm lipids and proteins were evaluated in each specimen. Selected cytokine levels were quantified using the ELISA method. Bacterial identification by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) mass spectrometry revealed that samples collected following two days of abstinence presented with a higher bacterial load and diversity, and a greater prevalence of potentially uropathogenic bacteria including Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Enterococcus faecalis. Only staphylococci and Escherichia coli remained present in specimens obtained after 2 h of abstinence. Whilst all samples accomplished the criteria set by WHO, a significantly higher motility (p < 0.05), membrane integrity (p < 0.05), mitochondrial membrane potential (p < 0.05), and DNA integrity (p < 0.0001) were detected following 2 h of ejaculatory abstinence. On the other hand, significantly higher ROS levels (p < 0.001), protein oxidation (p < 0.001), and lipid peroxidation (p < 0.01) accompanied by significantly higher concentrations of tumor necrosis factor alpha (p < 0.05), interleukin-6 (p < 0.01), and interferon gamma (p < 0.05) were observed in specimens collected after two days of abstinence. It may be summarized that shorter ejaculatory abstinence does not compromise sperm quality in normozoospermic men, while it contributes to a decreased occurrence of bacteria in semen which is accompanied by a lower probability of damage to spermatozoa by ROS or pro-inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: apoptosis; bacteria; ejaculatory abstinence; inflammation; oxidative stress; semen quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
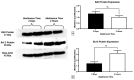
Similar articles
-
Possible Implications of Bacteriospermia on the Sperm Quality, Oxidative Characteristics, and Seminal Cytokine Network in Normozoospermic Men.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 4;23(15):8678. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158678. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955814 Free PMC article.
-
Role of seminal MDA, ROS, and antioxidants in cryopreservation and their kinetics under the influence of ejaculatory abstinence in bovine semen.Cryobiology. 2021 Feb;98:187-193. doi: 10.1016/j.cryobiol.2020.11.002. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Cryobiology. 2021. PMID: 33476643
-
One day is better than four days of ejaculatory abstinence for sperm function.Reprod Fertil. 2020 Oct 9;1(1):1-10. doi: 10.1530/RAF-20-0018. eCollection 2020 Jul. Reprod Fertil. 2020. PMID: 35128419 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of long and short ejaculatory abstinence on sperm parameters: a meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 May 17;15:1373426. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1373426. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38828413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Withania somnifera improves semen quality by combating oxidative stress and cell death and improving essential metal concentrations.Reprod Biomed Online. 2011 May;22(5):421-7. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2011.01.010. Epub 2011 Mar 8. Reprod Biomed Online. 2011. PMID: 21388887 Review.
Cited by
-
Short-interval second ejaculation improves sperm quality, blastocyst formation in oligoasthenozoospermic males in ICSI cycles: a time-lapse sibling oocytes study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 7;14:1250663. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1250663. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37745695 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes comparison of testicular versus ejaculated sperm for intracytoplasmic sperm injection in infertile men with high DNA fragmentation: updated systematic review and meta-analysis.Transl Androl Urol. 2023 Dec 31;12(12):1785-1802. doi: 10.21037/tau-23-415. Epub 2023 Dec 21. Transl Androl Urol. 2023. PMID: 38196694 Free PMC article.
-
Improved sperm DNA fragmentation levels in infertile men following very short abstinence of 3-4 hours.Transl Androl Urol. 2023 Oct 31;12(10):1487-1496. doi: 10.21037/tau-23-216. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Transl Androl Urol. 2023. PMID: 37969774 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in sperm quality by computer-assisted sperm analysis of 49,189 men during 2015-2021 in a fertility center from China.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 12;14:1194455. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1194455. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37529601 Free PMC article.
-
State-of-the-art approaches in the investigation of human seminal bacteriome using metagenomic methods.Front Reprod Health. 2025 Jun 5;7:1557912. doi: 10.3389/frph.2025.1557912. eCollection 2025. Front Reprod Health. 2025. PMID: 40538825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Milachich T., Dyulgerova-Nikolova D. The Sperm: Parameters and Evaluation. In: Sharma N., Chakrabarti S., Barak Y., Ellenbogen A., editors. Innovations in Assisted Reproduction Technology. 1st ed. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2020. pp. 1–20. - DOI
-
- World Health Organization . WHO Laboratory Manual for the Examination and Processing of Human Semen. 6th ed. WHO Press; Geneva, Switzerland: 2021. 276p
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

