Steroidogenic Factor 1, a Goldilocks Transcription Factor from Adrenocortical Organogenesis to Malignancy
- PMID: 36835002
- PMCID: PMC9959402
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043585
Steroidogenic Factor 1, a Goldilocks Transcription Factor from Adrenocortical Organogenesis to Malignancy
Abstract
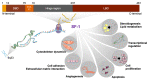
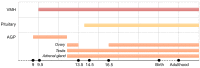
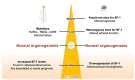
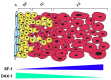
Steroidogenic factor-1 (SF-1, also termed Ad4BP; NR5A1 in the official nomenclature) is a nuclear receptor transcription factor that plays a crucial role in the regulation of adrenal and gonadal development, function and maintenance. In addition to its classical role in regulating the expression of P450 steroid hydroxylases and other steroidogenic genes, involvement in other key processes such as cell survival/proliferation and cytoskeleton dynamics have also been highlighted for SF-1. SF-1 has a restricted pattern of expression, being expressed along the hypothalamic-pituitary axis and in steroidogenic organs since the time of their establishment. Reduced SF-1 expression affects proper gonadal and adrenal organogenesis and function. On the other hand, SF-1 overexpression is found in adrenocortical carcinoma and represents a prognostic marker for patients' survival. This review is focused on the current knowledge about SF-1 and the crucial importance of its dosage for adrenal gland development and function, from its involvement in adrenal cortex formation to tumorigenesis. Overall, data converge towards SF-1 being a key player in the complex network of transcriptional regulation within the adrenal gland in a dosage-dependent manner.
Keywords: adrenal cortex; adrenocortical carcinoma; gene dosage; nuclear receptors; steroidogenesis; steroidogenic factor 1; transcription factors; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Zhang Z., Burch P.E., Cooney A.J., Lanz R.B., Pereira F.A., Wu J., Gibbs R.A., Weinstock G., Wheeler D.A. Genomic analysis of the nuclear receptor family: New insights into structure, regulation, and evolution from the rat genome. Genome Res. 2004;14:580–590. doi: 10.1101/gr.2160004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

