Prolonged Differentiation of Neuron-Astrocyte Co-Cultures Results in Emergence of Dopaminergic Neurons
- PMID: 36835019
- PMCID: PMC9959280
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043608
Prolonged Differentiation of Neuron-Astrocyte Co-Cultures Results in Emergence of Dopaminergic Neurons
Abstract
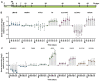
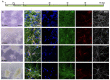
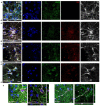
Dopamine is present in a subgroup of neurons that are vital for normal brain functioning. Disruption of the dopaminergic system, e.g., by chemical compounds, contributes to the development of Parkinson's disease and potentially some neurodevelopmental disorders. Current test guidelines for chemical safety assessment do not include specific endpoints for dopamine disruption. Therefore, there is a need for the human-relevant assessment of (developmental) neurotoxicity related to dopamine disruption. The aim of this study was to determine the biological domain related to dopaminergic neurons of a human stem cell-based in vitro test, the human neural progenitor test (hNPT). Neural progenitor cells were differentiated in a neuron-astrocyte co-culture for 70 days, and dopamine-related gene and protein expression was investigated. Expression of genes specific for dopaminergic differentiation and functioning, such as LMX1B, NURR1, TH, SLC6A3, and KCNJ6, were increasing by day 14. From day 42, a network of neurons expressing the catecholamine marker TH and the dopaminergic markers VMAT2 and DAT was present. These results confirm stable gene and protein expression of dopaminergic markers in hNPT. Further characterization and chemical testing are needed to investigate if the model might be relevant in a testing strategy to test the neurotoxicity of the dopaminergic system.
Keywords: dopaminergic neurons; human embryonic stem cells; in vitro; neurodegeneration; neurotoxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest that could have appeared to influence the content of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dopaminergic Neuronal Differentiation from the Forebrain-Derived Human Neural Stem Cells Induced in Cultures by Using a Combination of BMP-7 and Pramipexole with Growth Factors.Front Neural Circuits. 2016 Apr 20;10:29. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2016.00029. eCollection 2016. Front Neural Circuits. 2016. PMID: 27147976 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of functional dopaminergic neurons from human spermatogonial stem cells to rescue parkinsonian phenotypes.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019 Jun 27;10(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s13287-019-1294-x. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31248447 Free PMC article.
-
Nurr1 promotes neurogenesis of dopaminergic neuron and represses inflammatory factors in the transwell coculture system of neural stem cells and microglia.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018 Sep;24(9):790-800. doi: 10.1111/cns.12825. Epub 2018 Feb 15. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2018. PMID: 29450981 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Nurr1 in the development of dopaminergic neurons and Parkinson's disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2005 Sep-Oct;77(1-2):128-38. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2005.09.001. Epub 2005 Oct 21. Prog Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16243425 Review.
-
Neuron-Astrocyte Interactions in Parkinson's Disease.Cells. 2020 Dec 7;9(12):2623. doi: 10.3390/cells9122623. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33297340 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular and Functional Characterization of Different BrainSphere Models for Use in Neurotoxicity Testing on Microelectrode Arrays.Cells. 2023 Apr 27;12(9):1270. doi: 10.3390/cells12091270. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37174670 Free PMC article.
-
3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry.Nat Commun. 2023 Nov 24;14(1):7696. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-43586-4. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 38001146 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

