Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticle-Based Dexamethasone-Polypeptide Conjugates as Potential Intravitreal Delivery Systems
- PMID: 36835114
- PMCID: PMC9962198
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043702
Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticle-Based Dexamethasone-Polypeptide Conjugates as Potential Intravitreal Delivery Systems
Abstract
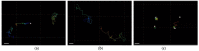
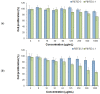
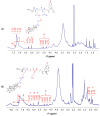
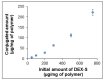
The use of dexamethasone for eye disease treatment is limited by its low solubility, bioavailability, and rapid elimination when applied topically. The covalent conjugation of dexamethasone with polymeric carriers is a promising strategy to overcome existing drawbacks. In this work, amphiphilic polypeptides capable of self-assembly into nanoparticles were proposed as potential delivery systems for intravitreal delivery. The nanoparticles were prepared and characterized using poly(L-glutamic acid-co-D-phenylalanine) and poly(L-lysine-co-D/L-phenylalanine) as well as poly(L-lysine-co-D/L-phenylalanine) covered with heparin. The critical association concentration for the polypeptides obtained was in the 4.2-9.4 μg/mL range. The hydrodynamic size of the formed nanoparticles was between 90 and 210 nm, and they had an index of polydispersity between 0.08 and 0.27 and an absolute zeta-potential value between 20 and 45 mV. The ability of nanoparticles to migrate in the vitreous humor was examined using intact porcine vitreous. Conjugation of DEX with polypeptides was performed by additional succinylation of DEX and activation of carboxyl groups introduced to react with primary amines in polypeptides. The structures of all intermediate and final compounds were verified by 1H NMR spectroscopy. The amount of conjugated DEX can be varied from 6 to 220 µg/mg of polymer. The hydrodynamic diameter of the nanoparticle-based conjugates was increased to 200-370 nm, depending on the polymer sample and drug loading. The release of DEX from the conjugates due to hydrolysis of the ester bond between DEX and the succinyl moiety was studied both in a buffer medium and a vitreous/buffer mixture (50/50, v/v). As expected, the release in the vitreous medium was faster. However, the release rate could be controlled in the range of 96-192 h by varying the polymer composition. In addition, several mathematical models were used to assess the release profiles and figure out how DEX is released.
Keywords: amphiphilic polypeptides; dexamethasone; drug delivery systems; intravitreal delivery; polymer-drug conjugates; self-assembled nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Novel Succinyl Chitosan-Dexamethasone Conjugates for Potential Intravitreal Dexamethasone Delivery.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 11;22(20):10960. doi: 10.3390/ijms222010960. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34681619 Free PMC article.
-
Mucoadhesive dexamethasone-glycol chitosan nanoparticles for ophthalmic drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2020 Feb 15;575:118943. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118943. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Int J Pharm. 2020. PMID: 31830575
-
Pharmacokinetics and tolerance study of intravitreal injection of dexamethasone-loaded nanoparticles in rabbits.Int J Nanomedicine. 2009;4:175-83. doi: 10.2147/ijn.s6428. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Int J Nanomedicine. 2009. PMID: 19774116 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles as a new generation therapeutic delivery platform: a review.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013 Nov;85(3 Pt A):427-43. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2013.07.002. Epub 2013 Jul 17. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2013. PMID: 23872180 Review.
-
Dexamethasone Conjugates: Synthetic Approaches and Medical Prospects.Biomedicines. 2021 Mar 27;9(4):341. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040341. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33801776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polypeptide-Based Systems: From Synthesis to Application in Drug Delivery.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Nov 20;15(11):2641. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15112641. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 38004619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Nanoparticle-Mediated Co-Delivery System: A Promising Strategy in Medical and Agricultural Field.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 7;24(6):5121. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065121. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Steroidal nanoformulations for the treatment of uveitis: potential, promises and future perspectives.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Feb 12;44(1):58. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03000-4. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38342799 Review.
-
Mitochondria targeted nanoparticles for the treatment of mitochondrial dysfunction-associated brain disorders.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Mar 12;13:1563701. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1563701. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40144395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linker-Free Hyaluronic Acid-Dexamethasone Conjugates: pH-Responsive Nanocarriers for Targeted Anti-Inflammatory Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 10;26(14):6608. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146608. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Madamsetty V.S., Mohammadinejad R., Uzieliene I., Nabavi N., Dehshahri A., García-Couce J., Tavakol S., Moghassemi S., Dadashzadeh A., Makvandi P., et al. Dexamethasone: Insights into Pharmacological Aspects, Therapeutic Mechanisms, and Delivery Systems. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022;8:1763–1790. - PubMed
-
- Gaballa S.A., Kompella U.B., Elgarhy O., Alqahtani A.M., Pierscionek B., Alany R.G., Abdelkader H. Corticosteroids in ophthalmology: Drug delivery innovations, pharmacology, clinical applications, and future perspectives. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2021;11:866–893. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

