Matrix Metalloproteinases in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 36835197
- PMCID: PMC9966421
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043786
Matrix Metalloproteinases in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Abstract
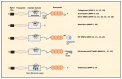
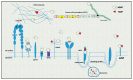
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are proteolytic enzymes that degrade proteins of the extracellular matrix and the basement membrane. Thus, these enzymes regulate airway remodeling, which is a major pathological feature of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Furthermore, proteolytic destruction in the lungs may lead to loss of elastin and the development of emphysema, which is associated with poor lung function in COPD patients. In this literature review, we describe and appraise evidence from the recent literature regarding the role of different MMPs in COPD, as well as how their activity is regulated by specific tissue inhibitors. Considering the importance of MMPs in COPD pathogenesis, we also discuss MMPs as potential targets for therapeutic intervention in COPD and present evidence from recent clinical trials in this regard.
Keywords: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs); tissue inhibitors of MMPs (TIMPs).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relationship between pulmonary matrix metalloproteinases and quantitative CT markers of small airways disease and emphysema in COPD.Thorax. 2016 Feb;71(2):126-32. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2015-207428. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Thorax. 2016. PMID: 26645414 Clinical Trial.
-
Distinct emphysema subtypes defined by quantitative CT analysis are associated with specific pulmonary matrix metalloproteinases.Respir Res. 2016 Jul 26;17(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0402-z. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27460105 Free PMC article.
-
The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in the pathophysiology of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): a therapeutic role for inhibitors of MMPs?Inflamm Res. 2003 Mar;52(3):95-100. doi: 10.1007/s000110300020. Inflamm Res. 2003. PMID: 12755372 Review.
-
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of MMPs in the respiratory tract: potential implications in asthma and other lung diseases.Eur J Pharmacol. 2006 Mar 8;533(1-3):133-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.12.082. Epub 2006 Feb 20. Eur J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16487964 Review.
-
Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016 Jun;64(3):177-93. doi: 10.1007/s00005-015-0375-5. Epub 2015 Nov 26. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2016. PMID: 26611761 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Qingjin Huatan decoction on pulmonary function and inflammatory mediators in acute exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Oct 18;15:1466677. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1466677. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39494348 Free PMC article.
-
Regorafenib prevents the development of emphysema in a murine elastase model.BMB Rep. 2023 Aug;56(8):439-444. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0072. BMB Rep. 2023. PMID: 37357536 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental immune network of airway lymphocytes and innate immune cells in patients with stable COPD.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 16;16:1614655. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1614655. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40589761 Free PMC article.
-
The Beneficial Effects of Soybean Proteins and Peptides on Chronic Diseases.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 7;15(8):1811. doi: 10.3390/nu15081811. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37111030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Qingjin Huatan decoction on pulmonary function and inflammatory mediators in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2025 May 7;20(5):e0322779. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322779. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40333888 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goodwin L. A Closer Look at Metalloproteinases. Nova Science Publisher Inc.; Hauppauge, NY, USA: 2019. p. 310.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

