Antibacterial Activity of Juglone Revealed in a Wound Model of Staphylococcus aureus Infection
- PMID: 36835350
- PMCID: PMC9963570
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24043931
Antibacterial Activity of Juglone Revealed in a Wound Model of Staphylococcus aureus Infection
Abstract
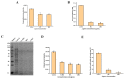
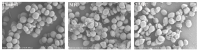
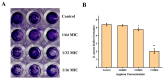
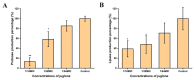
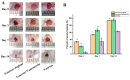
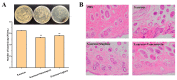
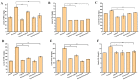
A serious problem currently facing the field of wound healing is bacterial infection, especially Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) infection. Although the application of antibiotics has achieved good effects, their irregular use has resulted in the emergence of drug-resistant strains. It is thus the purpose of this study to analyze whether the naturally extracted phenolic compound, juglone, can inhibit S. aureus in wound infection. The results show that the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of juglone against S. aureus was 1000 μg/mL. Juglone inhibited the growth of S. aureus by inhibiting membrane integrity and causing protein leakage. At sub-inhibitory concentrations, juglone inhibited biofilm formation, the expression of α-hemolysin, the hemolytic activity, and the production of proteases and lipases of S. aureus. When applied to infected wounds in Kunming mice, juglone (50 μL juglone with a concentration of 1000 μg/mL) significantly inhibited the number of S. aureus and had a significant inhibitory effect on the expression of inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β). Moreover, the juglone-treated group promoted wound healing. At the same time, in animal toxicity experiments, juglone had no obvious toxic effects on the main tissues and organs of mice, indicating that juglone has good biocompatibility and has the potential to be used in the treatment of wounds infected with S. aureus.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; biofilm; cell membrane integrity; juglone; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Unveiling the potential antibacterial action of acetylcysteine for managing Staphylococcus aureus wound infections: in vitro and in vivo study.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Apr 15;41(4):134. doi: 10.1007/s11274-025-04333-7. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40232590
-
Proteomic Analysis of the Antibacterial Mechanism of Action of Juglone against Staphylococcus aureus.Nat Prod Commun. 2016 Jun;11(6):825-7. Nat Prod Commun. 2016. PMID: 27534127
-
Potent synergistic combination of rosuvastatin and levofloxacin against Staphylococcus aureus: in vitro and in vivo study.J Appl Microbiol. 2021 Jul;131(1):182-196. doi: 10.1111/jam.14968. Epub 2020 Dec 30. J Appl Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 33326676
-
Evaluate the Effect of Zinc Oxide and Silver Nanoparticles on Biofilm and icaA Gene Expression in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolated From Burn Wound Infection.J Burn Care Res. 2020 Nov 30;41(6):1253-1259. doi: 10.1093/jbcr/iraa085. J Burn Care Res. 2020. PMID: 32479611
-
An overview on the antibacterial properties of juglone, naphthazarin, plumbagin and lawsone derivatives and their metal complexes.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Jun;162:114690. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114690. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 37075666 Review.
Cited by
-
Fabrication of Co-Assembly from Berberine and Tannic Acid for Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria Infection Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 21;15(7):1782. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071782. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37513970 Free PMC article.
-
Antibiofilm activity of Plumbagin against Staphylococcus aureus.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 7;15(1):7948. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-92435-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40055436 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Dual Bacteria-Imprinted Polymer Sensor for Highly Selective and Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Sep 3;13(9):868. doi: 10.3390/bios13090868. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37754102 Free PMC article.
-
New Chalcogen-Functionalized Naphthoquinones: Design, Synthesis, and Evaluation, In Vitro and In Silico, against Squamous Cell Carcinoma.ACS Omega. 2024 May 8;9(20):21948-21963. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c10134. eCollection 2024 May 21. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38799368 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, and In Vitro Evaluation of 4-(Arylchalcogenyl)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl-menadione: Exploring Their Potential Against Tuberculosis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 26;18(6):797. doi: 10.3390/ph18060797. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573194 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

