Comparison of Tomato Transcriptomic Profiles Reveals Overlapping Patterns in Abiotic and Biotic Stress Responses
- PMID: 36835470
- PMCID: PMC9961515
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24044061
Comparison of Tomato Transcriptomic Profiles Reveals Overlapping Patterns in Abiotic and Biotic Stress Responses
Abstract
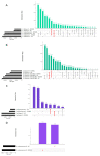
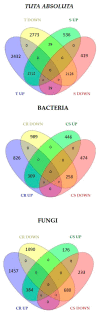
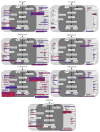
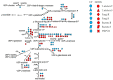
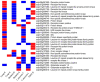
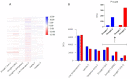
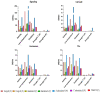
Until a few years ago, many studies focused on the transcriptomic response to single stresses. However, tomato cultivations are often constrained by a wide range of biotic and abiotic stress that can occur singularly or in combination, and several genes can be involved in the defensive mechanism response. Therefore, we analyzed and compared the transcriptomic responses of resistant and susceptible genotypes to seven biotic stresses (Cladosporium fulvum, Phytophthora infestans, Pseudomonas syringae, Ralstonia solanacearum, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV) and Tuta absoluta) and five abiotic stresses (drought, salinity, low temperatures, and oxidative stress) to identify genes involved in response to multiple stressors. With this approach, we found genes encoding for TFs, phytohormones, or participating in signaling and cell wall metabolic processes, participating in defense against various biotic and abiotic stress. Moreover, a total of 1474 DEGs were commonly found between biotic and abiotic stress. Among these, 67 DEGs were involved in response to at least four different stresses. In particular, we found RLKs, MAPKs, Fasciclin-like arabinogalactans (FLAs), glycosyltransferases, genes involved in the auxin, ET, and JA pathways, MYBs, bZIPs, WRKYs and ERFs genes. Detected genes responsive to multiple stress might be further investigated with biotechnological approaches to effectively improve plant tolerance in the field.
Keywords: cell wall; genome editing; phytohormones; plant stress; signaling; transcription factors; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kesawat M.S., Kherawat B.S., Singh A., Dey P., Kabi M., Debnath D., Saha D., Khandual A., Rout S., Manorama, et al. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the Brassinazole-Resistant (BZR) Gene Family and Its Expression in the Various Developmental Stage and Stress Conditions in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:8743. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kesawat M.S., Kherawat B.S., Singh A., Dey P., Routray S., Mohapatra C., Saha D., Ram C., Siddique K.H.M., Kumar A., et al. Genome-Wide Analysis and Characterization of the Proline-Rich Extensin-like Receptor Kinases (PERKs) Gene Family Reveals Their Role in Different Developmental Stages and Stress Conditions in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Plants. 2022;11:496. doi: 10.3390/plants11040496. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shao W., Chen W., Zhu X., Zhou X., Jin Y., Zhan C., Liu G., Liu X., Ma D., Qiao Y. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Wheat 14-3-3 Genes Unravels the Role of Tagrf6-a in Salt Stress Tolerance by Binding Myb Transcription Factor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:1904. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041904. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

