Overexpression of TgERF1, a Transcription Factor from Tectona grandis, Increases Tolerance to Drought and Salt Stress in Tobacco
- PMID: 36835560
- PMCID: PMC9961280
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24044149
Overexpression of TgERF1, a Transcription Factor from Tectona grandis, Increases Tolerance to Drought and Salt Stress in Tobacco
Abstract
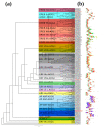
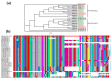
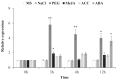
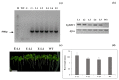
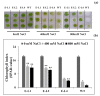
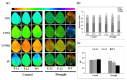
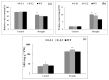
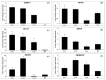
Teak (Tectona grandis) is one of the most important wood sources, and it is cultivated in tropical regions with a significant market around the world. Abiotic stresses are an increasingly common and worrying environmental phenomenon because it causes production losses in both agriculture and forestry. Plants adapt to these stress conditions by activation or repression of specific genes, and they synthesize numerous stress proteins to maintain their cellular function. For example, APETALA2/ethylene response factor (AP2/ERF) was found to be involved in stress signal transduction. A search in the teak transcriptome database identified an AP2/ERF gene named TgERF1 with a key AP2/ERF domain. We then verified that the TgERF1 expression is rapidly induced by Polyethylene Glycol (PEG), NaCl, and exogenous phytohormone treatments, suggesting a potential role in drought and salt stress tolerance in teak. The full-length coding sequence of TgERF1 gene was isolated from teak young stems, characterized, cloned, and constitutively overexpressed in tobacco plants. In transgenic tobacco plants, the overexpressed TgERF1 protein was localized exclusively in the cell nucleus, as expected for a transcription factor. Furthermore, functional characterization of TgERF1 provided evidence that TgERF1 is a promising candidate gene to be used as selective marker on plant breeding intending to improve plant stress tolerance.
Keywords: AP2/ERF family; Tectona grandis; drought stress; salt stress; tropical tree.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Zhang B., Su L., Hu B., Li L. Expression of AhDREB1, an AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Gene from Peanut, Is Affected by Histone Acetylation and Increases Abscisic Acid Sensitivity and Tolerance to Osmotic Stress in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018;19:1441. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fujita M., Fujita Y., Noutoshi Y., Takahashi F., Narusaka Y., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. Crosstalk between abiotic and biotic stress responses: A current view from the points of convergence in the stress signaling networks. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2006;9:436–442. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.05.014. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cheng M.C., Liao P.M., Kuo W.W., Lin T.P. The Arabidopsis ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTOR1 Regulates abiotic stress-responsive gene expression by binding to different cis-acting elements in response to different stress signals. Plant Physiol. 2013;162:1566–1582. doi: 10.1104/pp.113.221911. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

