Evidence for Existence of Multiple Functional Human Small RNAs Derived from Transcripts of Protein-Coding Genes
- PMID: 36835575
- PMCID: PMC9959880
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24044163
Evidence for Existence of Multiple Functional Human Small RNAs Derived from Transcripts of Protein-Coding Genes
Abstract
The human genome encodes a multitude of different noncoding transcripts that have been traditionally separated on the basis of their lengths into long (>200 nt) or small (<200 nt) noncoding RNAs. The functions, mechanisms of action, and biological relevance of the vast majority of both long and short noncoding transcripts remain unknown. However, according to the functional understanding of the known classes of long and small noncoding RNAs (sncRNAs) that have been shown to play crucial roles in multiple biological processes, it is generally assumed that many unannotated long and small transcripts participate in important cellular functions as well. Nevertheless, direct evidence of functionality is lacking for most noncoding transcripts, especially for sncRNAs that are often dismissed as stable degradation products of longer RNAs. Here, we developed a high-throughput assay to test the functionality of sncRNAs by overexpressing them in human cells. Surprisingly, we found that a significant fraction (>40%) of unannotated sncRNAs appear to have biological relevance. Furthermore, contrary to the expectation, the potentially functional transcripts are not highly abundant and can be derived from protein-coding mRNAs. These results strongly suggest that the small noncoding transcriptome can harbor multiple functional transcripts that warrant future studies.
Keywords: RNA dark matter; high-throughput phenotypic assay; noncoding RNA; short RNA; small RNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

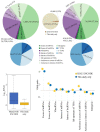
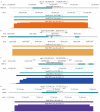




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

