Nicotine-Mediated Recruitment of GABAergic Neurons to a Dopaminergic Phenotype Attenuates Motor Deficits in an Alpha-Synuclein Parkinson's Model
- PMID: 36835612
- PMCID: PMC9960650
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24044204
Nicotine-Mediated Recruitment of GABAergic Neurons to a Dopaminergic Phenotype Attenuates Motor Deficits in an Alpha-Synuclein Parkinson's Model
Abstract
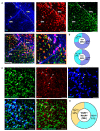
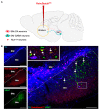
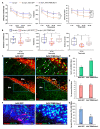
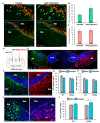
Previous work revealed an inverse correlation between tobacco smoking and Parkinson's disease (PD) that is associated with nicotine-induced neuroprotection of dopaminergic (DA) neurons against nigrostriatal damage in PD primates and rodent models. Nicotine, a neuroactive component of tobacco, can directly alter the activity of midbrain DA neurons and induce non-DA neurons in the substantia nigra (SN) to acquire a DA phenotype. Here, we investigated the recruitment mechanism of nigrostriatal GABAergic neurons to express DA phenotypes, such as transcription factor Nurr1 and DA-synthesizing enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH), and the concomitant effects on motor function. Wild-type and α-syn-overexpressing (PD) mice treated with chronic nicotine were assessed by behavioral pattern monitor (BPM) and immunohistochemistry/in situ hybridization to measure behavior and the translational/transcriptional regulation of neurotransmitter phenotype following selective Nurr1 overexpression or DREADD-mediated chemogenetic activation. We found that nicotine treatment led to a transcriptional TH and translational Nurr1 upregulation within a pool of SN GABAergic neurons in wild-type animals. In PD mice, nicotine increased Nurr1 expression, reduced the number of α-syn-expressing neurons, and simultaneously rescued motor deficits. Hyperactivation of GABA neurons alone was sufficient to elicit de novo translational upregulation of Nurr1. Retrograde labeling revealed that a fraction of these GABAergic neurons projects to the dorsal striatum. Finally, concomitant depolarization and Nurr1 overexpression within GABA neurons were sufficient to mimic nicotine-mediated dopamine plasticity. Revealing the mechanism of nicotine-induced DA plasticity protecting SN neurons against nigrostriatal damage could contribute to developing new strategies for neurotransmitter replacement in PD.
Keywords: alpha-synuclein; dopamine; neurotransmitter-switching; nicotine; substantia nigra; tyrosine-hydroxylase.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxytocin Protects Nigrostriatal Dopamine Signal via Activating GABAergic Circuit in the MPTP-Induced Parkinson's Disease Model.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Sep;11(36):e2310244. doi: 10.1002/advs.202310244. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39099429 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of tyrosine hydroxylase phenotype after AAV injection above substantia nigra: Caution in experimental models of Parkinson's disease.J Neurosci Res. 2019 Mar;97(3):346-361. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24363. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Neurosci Res. 2019. PMID: 30548446 Free PMC article.
-
Nurr1 in Parkinson's disease and related disorders.J Comp Neurol. 2006 Jan 20;494(3):495-514. doi: 10.1002/cne.20828. J Comp Neurol. 2006. PMID: 16320253 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of alpha-synuclein and dopamine metabolites in the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease: a case for the selective vulnerability of the substantia nigra.Acta Neuropathol. 2006 Aug;112(2):115-26. doi: 10.1007/s00401-006-0096-2. Epub 2006 Jun 22. Acta Neuropathol. 2006. PMID: 16791599 Review.
-
Reprint of: revisiting oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of Parkinson disease-resemblance to the effect of amphetamine drugs of abuse.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Sep;62:186-201. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.042. Epub 2013 Jun 3. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23743292 Review.
Cited by
-
Significance of nicotine and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in Parkinson's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 Mar 21;17:1535310. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1535310. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40191787 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generalized fear after acute stress is caused by change in neuronal cotransmitter identity.Science. 2024 Mar 15;383(6688):1252-1259. doi: 10.1126/science.adj5996. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Science. 2024. PMID: 38484078 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of the Protective Effects of Alkaloids against Alpha-synuclein Toxicity in Parkinson's Disease.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025;25(2):112-127. doi: 10.2174/0113895575306884240604065754. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 38874050 Review.
-
The Role of α7-Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 30;26(7):3210. doi: 10.3390/ijms26073210. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40244021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Glial Cells as Molecular Target for Parkinson's Disease.Cells. 2024 Mar 7;13(6):474. doi: 10.3390/cells13060474. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534318 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

