The Link between Prostanoids and Cardiovascular Diseases
- PMID: 36835616
- PMCID: PMC9962914
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24044193
The Link between Prostanoids and Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of global deaths, and many risk factors contribute to their pathogenesis. In this context, prostanoids, which derive from arachidonic acid, have attracted attention for their involvement in cardiovascular homeostasis and inflammatory processes. Prostanoids are the target of several drugs, but it has been shown that some of them increase the risk of thrombosis. Overall, many studies have shown that prostanoids are tightly associated with cardiovascular diseases and that several polymorphisms in genes involved in their synthesis and function increase the risk of developing these pathologies. In this review, we focus on molecular mechanisms linking prostanoids to cardiovascular diseases and we provide an overview of genetic polymorphisms that increase the risk for cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: arachidonic acid pathway; cardiovascular diseases; genetic polymorphisms; inflammation; prostanoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
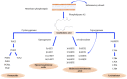
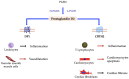
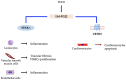



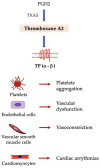

References
-
- Roth G.A., Mensah G.A., Johnson C.O., Addolorato G., Ammirati E., Baddour L.M., Barengo N.C., Beaton A.Z., Benjamin E.J., Benziger C.P., et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020;76:2982–3021. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Stanner S., Coe S., Frayn K. The Aetiology and Epidemiology of Cardiovascular Disease. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2018. pp. 1–28. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

