Best Practices for Comprehensive Annotation of Neuropeptides of Gryllus bimaculatus
- PMID: 36835690
- PMCID: PMC9960350
- DOI: 10.3390/insects14020121
Best Practices for Comprehensive Annotation of Neuropeptides of Gryllus bimaculatus
Abstract
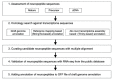
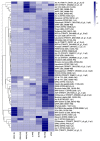
Genome annotation is critically important data that can support research. Draft genome annotations cover representative genes; however, they often do not include genes that are expressed only in limited tissues and stages, or genes with low expression levels. Neuropeptides are responsible for regulation of various physiological and biological processes. A recent study disclosed the genome draft of the two-spotted cricket Gryllus bimaculatus, which was utilized to understand the intriguing physiology and biology of crickets. Thus far, only two of the nine reported neuropeptides in G. bimaculatus were annotated in the draft genome. Even though de novo assembly using transcriptomic analyses can comprehensively identify neuropeptides, this method does not follow those annotations on the genome locus. In this study, we performed the annotations based on the reference mapping, de novo transcriptome assembly, and manual curation. Consequently, we identified 41 neuropeptides out of 43 neuropeptides, which were reported in the insects. Further, 32 of the identified neuropeptides on the genomic loci in G. bimaculatus were annotated. The present annotation methods can be applicable for the neuropeptide annotation of other insects. Furthermore, the methods will help to generate useful infrastructures for studies relevant to neuropeptides.
Keywords: Gryllus bimaculatus; draft genome annotation; functional annotation; genome annotation; neuropeptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

