Sporotrichosis Outbreak Due to Sporothrix brasiliensis in Domestic Cats in Magallanes, Chile: A One-Health-Approach Study
- PMID: 36836340
- PMCID: PMC9962391
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9020226
Sporotrichosis Outbreak Due to Sporothrix brasiliensis in Domestic Cats in Magallanes, Chile: A One-Health-Approach Study
Abstract
Sporotrichosis is an implantation mycosis with subcutaneo-lymphatic or, more rarely, a viscerally disseminated affection; it can be acquired through traumatic percutaneous inoculation of the fungus present in soil or plant matter, or by feline scratching. Among the causative agents, Sporothrix brasiliensis is considered the most virulent species with a high prevalence in Brazil and recently in Argentina.
Objective: To describe a S. brasiliensis outbreak in domestic and feral cats detected in the Magallanes region of southern Chile.
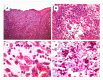
Materials and methods: Between the months of July and September 2022, three cats presented with suppurative subcutaneous lesions located mainly on the head and thoracic limbs. The cytology revealed the presence of yeasts with morphological characteristics suggestive of Sporothrix spp. The histopathology confirmed pyogranulomatous subcutaneous lesions associated with the presence of the same yeasts. The fungal culture followed by the partial gene sequence and analysis of the ITS region confirmed the diagnosis of the S. brasiliensis as the causative agent. The cats were treated with itraconazole associated in one case with potassium iodide. The evolution of the patients was favorable in all cases.
Conclusions: An outbreak caused by S. brasiliensis was detected in domestic and feral cats in austral Chile. The correct identification of this fungus and antifungigram is essential for treatment decisions and for designing dissemination control and prevention programs under a one health approach that consider the health of people, animals, and the environment.
Keywords: Sporothrix brasiliensis; cats; outbreak; zoonotic disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis in Argentina: Case report, molecular identification and in vitro susceptibility pattern to antifungal drugs.J Mycol Med. 2020 Apr;30(1):100908. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2019.100908. Epub 2019 Oct 15. J Mycol Med. 2020. PMID: 31732417
-
In vitro susceptibility of antifungal drugs against Sporothrix brasiliensis recovered from cats with sporotrichosis in Brazil.Med Mycol. 2016 Mar;54(3):275-9. doi: 10.1093/mmy/myv039. Epub 2015 Nov 21. Med Mycol. 2016. PMID: 26591009
-
Feline sporotrichosis due to Sporothrix brasiliensis: an emerging animal infection in São Paulo, Brazil.BMC Vet Res. 2014 Nov 19;10:269. doi: 10.1186/s12917-014-0269-5. BMC Vet Res. 2014. PMID: 25407096 Free PMC article.
-
Sporotrichosis in Children: Case series and Narrative Review.Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2022;16(2):33-46. doi: 10.1007/s12281-022-00429-x. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2022. PMID: 35284035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The threat of emerging and re-emerging pathogenic Sporothrix species.Mycopathologia. 2020 Oct;185(5):813-842. doi: 10.1007/s11046-020-00425-0. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Mycopathologia. 2020. PMID: 32052359 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenging frontiers: Canine sporotrichosis due to Sporothrix brasiliensis, first case in Chile.Med Mycol Case Rep. 2024 Mar 8;44:100632. doi: 10.1016/j.mmcr.2024.100632. eCollection 2024 Jun. Med Mycol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38550851 Free PMC article.
-
Current Progress in Sporothrix brasiliensis Basic Aspects.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Apr 29;9(5):533. doi: 10.3390/jof9050533. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37233242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bimodal distribution of azole susceptibility in Sporothrix brasiliensis isolates in Brazil.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024 Apr 3;68(4):e0162023. doi: 10.1128/aac.01620-23. Epub 2024 Feb 22. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2024. PMID: 38385701 Free PMC article.
-
High-Throughput Microsatellite Markers Development for Genetic Characterization of Emerging Sporothrix Species.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Mar 14;9(3):354. doi: 10.3390/jof9030354. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36983522 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR-based tools for targeted genetic manipulation in pathogenic Sporothrix species.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Sep 14;11(5):e0507822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.05078-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37707447 Free PMC article.
References
-
- PAHO Sporothrix brasiliensis, an Emerging Fungal Pathogen, Notable for Its Zoonotic Transmission and Epidemic Potential for Human and Animal Health in the Americas. [(accessed on 15 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.someve.com.ar/images/noticias/2019/S-brasiliensis_lasAmerica....
-
- Sizar O., Talati R. Sporotrichosis. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2022. - PubMed
-
- Fichman V., Freitas D.F.S., Valle A.C.F.D., de Souza R.V., Curi A.L.L., Valete-Rosalino C.M., de Macedo P.M., Varon A.G., Figueiredo-Carvalho M.H.G., Almeida-Silva F., et al. Severe Sporotrichosis Treated with Amphotericin B: A 20-Year Cohort Study in an Endemic Area of Zoonotic Transmission. J. Fungi. 2022;8:469. doi: 10.3390/jof8050469. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

