Invasive Aspergillosis after Renal Transplantation
- PMID: 36836369
- PMCID: PMC9963524
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9020255
Invasive Aspergillosis after Renal Transplantation
Abstract
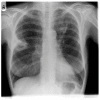
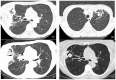
Over 95,000 renal transplantation procedures were completed in 2021. Invasive aspergillosis (IA) affects about 1 in 250 to 1 in 43 renal transplant recipients. About 50% of cases occur in the first 6 months after transplantation; the median time of onset is nearly 3 years. Major risk factors for IA include old age, diabetes mellitus (especially if prior diabetic nephropathy), delayed graft function, acute graft rejection, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cytomegalovirus disease, and neutropenia. Hospital construction, demolition activities, and residential refurbishments also increase the risk. Parenchymal pulmonary infection is the most common (~75%), and bronchial, sinus, cerebral, and disseminated disease are less common. Typical pulmonary features of fever, dyspnea, cough, and hemoptysis are seen in most patients, but 20% have non-specific general features of illness. Non-specific infiltrates and pulmonary nodules are the commonest radiological features, with bilateral disease carrying a worse prognosis. Bronchoscopy for direct microscopy, fungal culture, and Aspergillus antigen are the fastest means of establishing the diagnosis; a positive serum Aspergillus antigen presages a worse outcome. Standard therapy includes voriconazole, isavuconazole, or posaconazole, with great attention necessary to assess likely drug-drug interactions. Liposomal amphotericin B and echinocandins are less effective. A reduction in or stopping immunosuppression needs careful consideration, given the overall mortality of IA in renal-transplanted patients; continuing corticosteroid after the diagnosis of IA increases mortality by 2.5 times. Surgical resection or the addition of a gamma interferon should also be considered.
Keywords: antifungals; immunosuppression; invasive aspergillosis; renal transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
L.S.M.S. declares no conflict of interest. D.W.D. and family hold Founder shares in F2G Ltd., a University of Manchester spin-out antifungal discovery company, and share options in TFF Pharma. He acts or has recently acted as a consultant to Pulmatrix, Pulmocide, Biosergen, TFF Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, Omega, Novacyt, Rostra Therapeutics, MucPharm and Cipla. He sat on the DSMB for a SARS-CoV2 vaccine trial and chairs a Data Review Committee for Pulmocide. In the last 3 years, he has been paid for talks on behalf of Hikma, Gilead, BioRad, Basilea, Mylan, and Pfizer. He is a longstanding member of the Infectious Disease Society of America Aspergillosis Guidelines group, the European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases Aspergillosis Guidelines group, and he recently joined the One World Guideline for Aspergillosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[The clinical monitoring of invasive aspergillosis in surgical intensive care unit during 10 years].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014 Sep;26(9):634-8. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2014.09.006. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2014. PMID: 25230864 Chinese.
-
Pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with AIDS. Clinical and radiographic correlations.Chest. 1994 Jan;105(1):37-44. doi: 10.1378/chest.105.1.37. Chest. 1994. PMID: 8275779
-
Liposomal amphotericin B: a review of its use as empirical therapy in febrile neutropenia and in the treatment of invasive fungal infections.Drugs. 2009;69(3):361-92. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200969030-00010. Drugs. 2009. PMID: 19275278 Review.
-
[Fever and cavitary infiltrate in a renal transplant recipient].Nefrologia. 2004;24 Suppl 3:16-20. Nefrologia. 2004. PMID: 15219062 Spanish.
-
Invasive aspergillosis in liver transplant recipients.Transpl Infect Dis. 2023 Jun;25(3):e14049. doi: 10.1111/tid.14049. Epub 2023 Mar 16. Transpl Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36929539 Review.
Cited by
-
Management of Polypharmacy and Potential Drug-Drug Interactions in Patients with Pulmonary Aspergillosis: A 2-Year Study of a Multidisciplinary Outpatient Clinic.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Jan 26;10(2):107. doi: 10.3390/jof10020107. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392779 Free PMC article.
-
Fungal Infections in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Comprehensive Narrative Review.Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 18;13(1):207. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13010207. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 39858974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent developments in Aspergillus fumigatus research: diversity, drugs, and disease.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2025 Mar 27;89(1):e0001123. doi: 10.1128/mmbr.00011-23. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2025. PMID: 39927770 Review.
-
Persistent fever after coronavirus disease 2019 in liver/kidney transplant recipient.Transpl Infect Dis. 2024 Jun;26(3):e14271. doi: 10.1111/tid.14271. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Transpl Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38605533 Free PMC article.
-
The epidemiological characteristics of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis and risk factors for treatment failure: a retrospective study.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Nov 8;24(1):559. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03381-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39511508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li Z.W., Peng F.H., Yan M., Liang W., Liu X.L., Wu Y.Q., Lin X.B., Tan S.L., Wang F., Xu P., et al. Impact of CYP2C19 genotype and liver function on voriconazole pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients. Ther. Drug Monit. 2017;39:422–428. doi: 10.1097/FTD.0000000000000425. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Seok H., Huh K., Cho S.Y., Kang C.I., Chung D.R., Huh W.S., Park J.B., Peck K.R. Risk factors for development and mortality of invasive pulmonary Aspergillosis in kidney transplantation recipients. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020;39:1543–1550. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-03871-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mouloudi E., Massa E., Georgiadou E., Iosifidis E., Katsika E., Rembelakos G., Gakis D., Imvrios G., Papanikolaou V., Papadopoulos S., et al. Infections related to renal transplantation requiring intensive care admission: A 20-year study. Transplant. Proc. 2012;44:2721–2723. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2012.09.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- López-Medrano F., Fernández-Ruiz M., Silva J.T., Carver P.L., van Delden C., Merino E., Pérez-Saez M.J., Montero M., Coussement J., de Abreu M.M., et al. Clinical presentation and determinants of mortality of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in kidney transplant recipients: A multinational cohort study. Am. J. Transplant. 2016;16:3220–3234. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13837. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Global Observatory on Donation and Transplantation. [(accessed on 11 January 2022)]. Available online: www.transplant-observatory.org/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

