Small Signals Lead to Big Changes: The Potential of Peptide-Induced Resistance in Plants
- PMID: 36836379
- PMCID: PMC9965805
- DOI: 10.3390/jof9020265
Small Signals Lead to Big Changes: The Potential of Peptide-Induced Resistance in Plants
Abstract
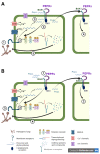
The plant immunity system is being revisited more and more and new elements and roles are attributed to participating in the response to biotic stress. The new terminology is also applied in an attempt to identify different players in the whole scenario of immunity: Phytocytokines are one of those elements that are gaining more attention due to the characteristics of processing and perception, showing they are part of a big family of compounds that can amplify the immune response. This review aims to highlight the latest findings on the role of phytocytokines in the whole immune response to biotic stress, including basal and adaptive immunity, and expose the complexity of their action in plant perception and signaling events.
Keywords: induced resistance; peptides; phytocytokines; plant immunity; priming.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

