Sex-Related Differences and Factors Associated with Peri-Procedural and 1 Year Mortality in Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia Patients from the CLIMATE Italian Registry
- PMID: 36836550
- PMCID: PMC9959358
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm13020316
Sex-Related Differences and Factors Associated with Peri-Procedural and 1 Year Mortality in Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia Patients from the CLIMATE Italian Registry
Abstract
Background: Identifying sex-related differences/variables associated with 30 day/1 year mortality in patients with chronic limb-threatening ischemia (CLTI).
Methods: Multicenter/retrospective/observational study. A database was sent to all the Italian vascular surgeries to collect all the patients operated on for CLTI in 2019. Acute lower-limb ischemia and neuropathic-diabetic foot are not included.
Follow-up: One year. Data on demographics/comorbidities, treatments/outcomes, and 30 day/1 year mortality were investigated.
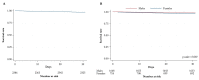
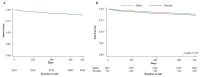
Results: Information on 2399 cases (69.8% men) from 36/143 (25.2%) centers. Median (IQR) age: 73 (66-80) and 79 (71-85) years for men/women, respectively (p < 0.0001). Women were more likely to be over 75 (63.2% vs. 40.1%, p = 0.0001). More men smokers (73.7% vs. 42.2%, p < 0.0001), are on hemodialysis (10.1% vs. 6.7%, p = 0.006), affected by diabetes (61.9% vs. 52.8%, p < 0.0001), dyslipidemia (69.3% vs. 61.3%, p < 0.0001), hypertension (91.8% vs. 88.5%, p = 0.011), coronaropathy (43.9% vs. 29.4%, p < 0.0001), bronchopneumopathy (37.1% vs. 25.6%, p < 0.0001), underwent more open/hybrid surgeries (37.9% vs. 28.8%, p < 0.0001), and minor amputations (22% vs. 13.7%, p < 0.0001). More women underwent endovascular revascularizations (61.6% vs. 55.2%, p = 0.004), major amputations (9.6% vs. 6.9%, p = 0.024), and obtained limb-salvage if with limited gangrene (50.8% vs. 44.9%, p = 0.017). Age > 75 (HR = 3.63, p = 0.003) is associated with 30 day mortality. Age > 75 (HR = 2.14, p < 0.0001), nephropathy (HR = 1.54, p < 0.0001), coronaropathy (HR = 1.26, p = 0.036), and infection/necrosis of the foot (dry, HR = 1.42, p = 0.040; wet, HR = 2.04, p < 0.0001) are associated with 1 year mortality. No sex-linked difference in mortality statistics.
Conclusion: Women exhibit fewer comorbidities but are struck by CLTI when over 75, a factor associated with short- and mid-term mortality, explaining why mortality does not statistically differ between the sexes.
Keywords: age; chronic limb-threatening ischemia; limb salvage; outcome; sex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Conte M.S. Lower Extremity Arterial Occlusive Disease Epidemiology and Natural History. In: Sidawy A.P., Perler B.A., editors. Rutherford’s Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy. 9th ed. Volume 2. Elsevier-OHCE; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2018. pp. 1368–1376.
-
- Wu B., Lancaster E.M., Ramirez J.L., Zarkowsky D.S., Reyzelman A.M., Gasper W.J., Conte M.S., Hiramoto J.S. Increased Reintervention after Infrainguinal Revascularization for Chronic Limb-Threatening Ischemia in Women. Ann. Vasc. Surg. 2020;69:307–316. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2020.06.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Makowski L., Köppe J., Engelbertz C., Kühnemund L., Fischer A.J., A Lange S., Dröge P., Ruhnke T., Günster C., Malyar N., et al. Sex-related differences in treatment and outcome of chronic limb-threatening ischaemia: A real-world cohort. Eur. Heart J. 2022;43:1759–1770. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac016. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anantha-Narayanan M., Doshi R.P., Patel K., Sheikh A.B., Llanos-Chea F., Abbott J.D., Shishehbor M.H., Guzman R.J., Hiatt W.R., Duval S., et al. Contemporary Trends in Hospital Admissions and Outcomes in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes. 2021;14:e007539. doi: 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.120.007539. - DOI - PubMed