Dietary Supplements with Proline-A Comprehensive Assessment of Their Quality
- PMID: 36836622
- PMCID: PMC9958592
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020263
Dietary Supplements with Proline-A Comprehensive Assessment of Their Quality
Abstract
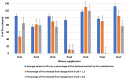
Dietary supplements are food products commonly used worldwide to obtain nutritional and physiological effects. They can contain a wide variety of active substances and can be administered for health and disease. Their use can be beneficial if justified, and their quality is adequate. Unfortunately, data on the quality of supplements is scarce. As part of this work, we assess the quality of seven dietary supplements containing proline. The preparations were produced in the EU and the USA. The quality assessment consisted of the detection of potential impurities, the determination of the content of the main ingredient, and the release of proline. The technique used to analyse impurities and proline (Pro) content was liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. We detected five contaminants. The main ingredient content was in the range of 73-121% in capsules and 103-156% in tablets. Five of the seven analysed dietary supplements released below 80% Pro (for each tablet/capsule at pH 1.2). One of the supplements may be inactive because a very low release of Pro was reported. The results, we hope, will increase consumer awareness of the quality of these preparations and result in a change in the regulations governing the marketing of these preparations, at least by making release testing mandatory.
Keywords: dietary supplement; dissolution test; food supplement analysis; proline; quality control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry in Quality Assessment of Dietary Supplements-A Case Study of Tryptophan Supplements: Release Assay, Targeted and Untargeted Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 4;15(4):448. doi: 10.3390/ph15040448. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455446 Free PMC article.
-
Melamine contamination in nutritional supplements--Is it an alarm bell for the general consumer, athletes, and 'Weekend Warriors'?Nutr J. 2015 Jul 17;14:69. doi: 10.1186/s12937-015-0055-7. Nutr J. 2015. PMID: 26182916 Free PMC article.
-
The Content of Mercury in Herbal Dietary Supplements.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018 Sep;185(1):236-243. doi: 10.1007/s12011-018-1240-2. Epub 2018 Jan 17. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018. PMID: 29344817 Free PMC article.
-
Current trends in the analysis and quality control of food supplements based on plant extracts.Anal Chim Acta. 2018 Dec 7;1036:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2018.08.017. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Anal Chim Acta. 2018. PMID: 30253819 Review.
-
[Food supplements : Legal requirements, borderline issues and other aspects].Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2017 Mar;60(3):260-267. doi: 10.1007/s00103-016-2499-0. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2017. PMID: 28070624 Review. German.
References
-
- Marasco G., Cirota G.G., Rossini B., Lungaro L., Di Biase A.R., Colecchia A., Volta U., De Giorgio R., Festi D., Caio G. Probiotics, prebiotics and other dietary supplements for gut microbiota modulation in celiac disease patients. Nutrients. 2020;12:2674. doi: 10.3390/nu12092674. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

