Characteristics, Roles and Applications of Proteinaceous Elicitors from Pathogens in Plant Immunity
- PMID: 36836624
- PMCID: PMC9960299
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020268
Characteristics, Roles and Applications of Proteinaceous Elicitors from Pathogens in Plant Immunity
Abstract
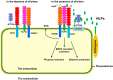
In interactions between pathogens and plants, pathogens secrete many molecules that facilitate plant infection, and some of these compounds are recognized by plant pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), which induce immune responses. Molecules in both pathogens and plants that trigger immune responses in plants are termed elicitors. On the basis of their chemical content, elicitors can be classified into carbohydrates, lipopeptides, proteinaceous compounds and other types. Although many studies have focused on the involvement of elicitors in plants, especially on pathophysiological changes induced by elicitors in plants and the mechanisms mediating these changes, there is a lack of up-to-date reviews on the characteristics and functions of proteinaceous elicitors. In this mini-review, we provide an overview of the up-to-date knowledge on several important families of pathogenic proteinaceous elicitors (i.e., harpins, necrosis- and ethylene-inducing peptide 1 (nep1)-like proteins (NLPs) and elicitins), focusing mainly on their structures, characteristics and effects on plants, specifically on their roles in plant immune responses. A solid understanding of elicitors may be helpful to decrease the use of agrochemicals in agriculture and gardening, generate more resistant germplasms and increase crop yields.
Keywords: NLPs; elicitin; elicitors; harpin; immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Extracellular Recognition of Oomycetes during Biotrophic Infection of Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2016 Jun 21;7:906. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2016.00906. eCollection 2016. Front Plant Sci. 2016. PMID: 27446136 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and Characterization of Nep1-Like Proteins From the Grapevine Downy Mildew Pathogen Plasmopara viticola.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Feb 13;11:65. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.00065. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32117400 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of microbial bio-agents as elicitors in plant defense mechanism under biotic stress: A review.Curr Res Microb Sci. 2021 Aug 8;2:100054. doi: 10.1016/j.crmicr.2021.100054. eCollection 2021 Dec. Curr Res Microb Sci. 2021. PMID: 34841345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The oligomeric states of elicitins affect the hypersensitive response and resistance in tobacco.J Exp Bot. 2021 Apr 2;72(8):3219-3234. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erab011. J Exp Bot. 2021. PMID: 33475728
-
Harpins, multifunctional proteins secreted by gram-negative plant-pathogenic bacteria.Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013 Oct;26(10):1115-22. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-02-13-0050-CR. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 2013. PMID: 23745678 Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct immune pathways activated by harpin proteins in Sorghum bicolor.Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025 May;31(5):785-793. doi: 10.1007/s12298-025-01601-6. Epub 2025 Jun 3. Physiol Mol Biol Plants. 2025. PMID: 40568477
-
Protein elicitor PeVn1 induces resistance to Botrytis cinerea in strawberry and differential transcriptomic analysis.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 13;16:1541448. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1541448. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40432975 Free PMC article.
-
The Past, Present, and Future of Plant Activators Targeting the Salicylic Acid Signaling Pathway.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 23;15(9):1237. doi: 10.3390/genes15091237. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39336828 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

