How Does the Level of Physical Activity Influence Eating Behavior? A Self-Determination Theory Approach
- PMID: 36836655
- PMCID: PMC9961293
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020298
How Does the Level of Physical Activity Influence Eating Behavior? A Self-Determination Theory Approach
Abstract
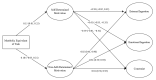
Physical activity and diet are two predominant determinants of population health status that may influence each other. Physical activity has been identified as a behavior that may lead to a healthier diet and regulates eating behaviors. This research aimed to investigate how the level of physical activity is associated with the motivation related to eating behaviors and, consequently, the eating style individuals have on a daily basis. This was a cross-sectional study in which participants completed an online questionnaire that assessed the following variables: the level of physical activity, the motivation toward eating behavior, and the type of eating behavior. In total, 440 individuals (180 men and 260 women) who regularly exercised in gyms and fitness centers aged between 19 and 64 years (M = 33.84; SD = 10.09) took part in the study. The data were collected following the Declaration of Helsinki and with the approval of the Ethics Committee of the Polytechnic of Leiria. For the statistical analysis, mean and standard deviations were first calculated, as well as bivariate correlations between all the variables of interest. Then, structural equation model analyses were performed considering the levels of physical activity as the independent variable, motivations toward eating behavior as the mediators, and eating styles as the dependent variables. It was concluded that a greater level of physical activity leads to a more self-determined type of eating regulation, which in turn results in less constricted eating behaviors that are influenced by external factors and emotional factors.
Keywords: eating behavior; physical activity; regulation of eating behavior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources