Secukinumab and Black Garlic Downregulate OPG/RANK/RANKL Axis and Devitalize Myocardial Interstitial Fibrosis Induced by Sunitinib in Experimental Rats
- PMID: 36836664
- PMCID: PMC9962443
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020308
Secukinumab and Black Garlic Downregulate OPG/RANK/RANKL Axis and Devitalize Myocardial Interstitial Fibrosis Induced by Sunitinib in Experimental Rats
Abstract
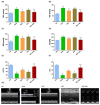
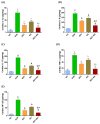
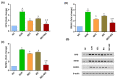
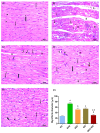
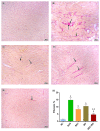
Sunitinib has been associated with several cardiotoxic effects such as cardiac fibrosis. The present study was designed to explore the role of interleukin (IL)-17 in sunitinib-induced myocardial fibrosis (MF) in rats and whether its neutralization and/or administration of black garlic (BG), a form of fermented raw garlic (Allium sativum L.), could extenuate this adverse effect. Male Wistar albino rats received sunitinib (25 mg/kg three times a week, orally) and were co-treated with secukinumab (3 mg/kg, subcutaneously, three times total) and/or BG (300 mg/kg/day, orally) for four weeks. Administration of sunitinib induced significant increase in cardiac index, cardiac inflammatory markers, and cardiac dysfunction that were ameliorated by both secukinumab and BG, and to a preferable extent, with the combined treatment. Histological examination revealed disruption in the myocardial architecture and interstitial fibrosis in cardiac sections of the sunitinib group, which were reversed by both secukinumab and BG treatments. Both drugs and their co-administration restored normal cardiac functions, downregulated cardiac inflammatory cytokines, mainly IL-17 and NF-κB, along with increasing the MMP1/TIMP1 ratio. Additionally, they attenuated sunitinib-induced upregulation of the OPG/RANK/RANKL axis. These findings highlight another new mechanism through which sunitinib can induce interstitial MF. The current results propose that neutralizing IL-17 by secukinumab and/or supplementation with BG can be a promising therapeutic approach for ameliorating sunitinib-induced MF.
Keywords: IL-17; OPG/RANK/RANKL; black garlic; interstitial myocardial fibrosis; secukinumab; sunitinib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

