Ephedra alata Subsp. Alenda as a Novel Source of Bioactive Phytochemicals: Characterization Based on the Mass Spectrometry and Profiling of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
- PMID: 36836680
- PMCID: PMC9961366
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020323
Ephedra alata Subsp. Alenda as a Novel Source of Bioactive Phytochemicals: Characterization Based on the Mass Spectrometry and Profiling of Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Abstract
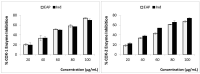
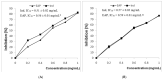
The aim of the present study was to examine, for the first time, the phytochemical content of Ephedra alata pulp extract (EAP) and explore its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities. High-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-QTOF/MS) was used for phytochemical analysis and three in vitro antioxidant assays together with three in vitro anti-inflammatory tests were used for the assessment of biological activity. The HPLC-ESI-QTOF/MS analysis revealed the presence of 42 metabolites, including flavonoids, sphingolipides, fatty acids, ephedrine derivatives, and amino acid derivatives. In vitro findings revealed that EAP has interesting 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), superoxide, and ferrous ion chelating capacities (IC50 values were 0.57 mg/mL, 0.55 mg/mL, and 0.51 mg/mL for DPPH, superoxide radical, and ferrous ion, respectively). Furthermore, EAP showed a noticeable anti-inflammatory ability by inhibiting the two cyclooxygenase isoforms, COX-1 and COX-2 (IC50 of 59.1 and 58.8 µg/mL for COX-1 and COX-2, respectively), preventing protein denaturation (IC50 = 0.51 mg/mL), and protecting membrane stabilization (IC50 = 0.53 mg/mL). The results highlighted the use of Ephedra alata pulp as a potential source of natural compounds with therapeutic effects for the management of inflammatory disorders.
Keywords: COX1 and COX2; Ephedra alata; anti-inflammatory; antioxidants; high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC–ESI–QTOF/MS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Phytochemical, biological, and computational investigations of Ephedra alata Decne. growing in salinity conditions of Arabian Peninsula.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 23;14(1):21987. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69607-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39313524 Free PMC article.
-
HPLC-DAD-ESI/MS profiles of bioactive compounds, antioxidant and anticholinesterase activities of Ephedra alata subsp. alenda growing in Algeria.Nat Prod Res. 2022 Nov;36(22):5910-5915. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2021.2024184. Epub 2022 Jan 12. Nat Prod Res. 2022. PMID: 35019791
-
Investigation of the phytochemical profiling and antioxidant, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, and MDA-MB-231 cell line antiproliferative potentials of extracts from Ephedra alata Decne.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 6;14(1):18240. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65561-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39107351 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Screening, Antioxidant Potential, and LC-ESI-MS Profiling of Ephedra alata and Ephedra altissima Seeds Naturally Growing in Tunisia.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023 Oct;195(10):5903-5915. doi: 10.1007/s12010-023-04370-8. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36719522 Free PMC article.
-
Forced degradation and impurity profiling: recent trends in analytical perspectives.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013 Dec;86:11-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2013.07.013. Epub 2013 Jul 31. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2013. PMID: 23969330 Review.
Cited by
-
Ephedra fragilis plant extract: A groundbreaking corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic environments - electrochemical, EDX, DFT, and Monte Carlo studies.Open Life Sci. 2025 Mar 26;20(1):20221050. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-1050. eCollection 2025. Open Life Sci. 2025. PMID: 40177419 Free PMC article.
-
Pirimicarb Induction of Behavioral Disorders and of Neurological and Reproductive Toxicities in Male Rats: Euphoric and Preventive Effects of Ephedra alata Monjauzeana.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 7;16(3):402. doi: 10.3390/ph16030402. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36986501 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical, biological, and computational investigations of Ephedra alata Decne. growing in salinity conditions of Arabian Peninsula.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 23;14(1):21987. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-69607-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39313524 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mahnashi M.H., Alyami B.A., Alqahtani Y.S., Jan M.S., Rashid U., Sadiq A., Alqarni A.O. Phytochemical Profiling of Bioactive Compounds, Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Potentials of Habenaria digitata Lindl.: Molecular Docking Based Synergistic Effect of the Identified Compounds. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021;273:113976. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113976. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tir M., Feriani A., Labidi A., Mufti A., Saadaoui E., Nasri N., Khaldi A., El Cafsi M., Tlili N. Protective effects of phytochemicals of Capparis spinosa seeds with cisplatin and CCl4 toxicity in mice. Food Biosci. 2019;28:42–48. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2019.01.002. - DOI
-
- Hajhashemi V., Ghanadian M., Palizaban A., Mahnam K., Eshaghi H., Gheisari B., Sadeghi-Aliabadi H. Cycloarta-23-Ene-3beta,25-Diol a Pentacyclic Steroid from Euphorbia Spinidens, as COX Inhibitor with Molecular Docking, and In Vivo Study of Its Analgesic and Anti-Inflammatory Activities in Male Swiss Mice and Wistar Rats. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2020;150:106473. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2020.106473. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Abd El-Karim S.S., Mohamed H.S., Abdelhameed M.F., Amr AE G.E., Almehizia A.A., Nossier E.S. Design, Synthesis and Molecular Docking of New Pyrazole-Thiazolidinones as Potent Anti-Inflammatory and Analgesic Agents with TNF-α Inhibitory Activity. Bioorganic Chem. 2021;111:104827. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.104827. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

