Plant Extracts and SARS-CoV-2: Research and Applications
- PMID: 36836744
- PMCID: PMC9965937
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020386
Plant Extracts and SARS-CoV-2: Research and Applications
Abstract
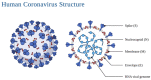
The recent pandemic of COVID-19 caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus has brought upon the world an unprecedented challenge. During its acute dissemination, a rush for vaccines started, making the scientific community come together and contribute to the development of efficient therapeutic agents and vaccines. Natural products have been used as sources of individual molecules and extracts capable of inhibiting/neutralizing several microorganisms, including viruses. Natural extracts have shown effective results against the coronavirus family, when first tested in the outbreak of SARS-CoV-1, back in 2002. In this review, the relationship between natural extracts and SARS-CoV is discussed, while also providing insight into misinformation regarding the use of plants as possible therapeutic agents. Studies with plant extracts on coronaviruses are presented, as well as the main inhibition assays and trends for the future regarding the yet unknown long-lasting effects post-infection with SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; anti-viral agents; pandemic; secondary metabolism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Al-Sanea M.M., Abelyan N., Abdelgawad M.A., Musa A., Ghoneim M.M., Al-Warhi T., Aljaeed N., Alotaibi O.J., Alnusaire T.S., Abdelwahab S.F., et al. Strawberry and ginger silver nanoparticles as potential inhibitors for SARS-CoV-2 sssisted by in silico modeling and metabolic profiling. Antibiotics. 2021;10:824. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10070824. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

