Ferulic Acid Treats Gastric Ulcer via Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
- PMID: 36836745
- PMCID: PMC9959638
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020388
Ferulic Acid Treats Gastric Ulcer via Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Abstract
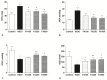
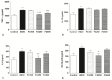
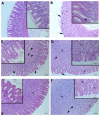
(1) Background: The aim of the present study was to evaluate the gastroprotective potential of ferulic acid (FA) on indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in rats with macroscopic and microscopic examinations along with biochemical assays. (2) Methods: After 24 h starvation, the ulcer was induced in male Sprague-Dawley rats by subcutaneous indomethacin (25 mg/kg) injection. Fifteen minutes after ulcer induction, rats were treated with either tween 80 or FA. FA was given by oral gavage at 100 mg/kg, 250 mg/kg, and 500 mg/kg. In the fourth hour, rats were euthanized and collected gastric samples were evaluated macroscopically and microscopically. Antioxidant parameters including malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione (GSH), superoxide dismutase (SOD), and inflammatory parameters comprising of myeloperoxidase (MPO), Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF)-α, Interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6 and Nuclear Factor Kappa-B (NF-κB) p65 levels were also determined. (3) Results: Indomethacin injection significantly increased the macroscopic and microscopic scores. In addition, it increased the gastric MDA, MPO, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and NF-κB p65 levels but reduced SOD and GSH content. Treatment with FA significantly improved the gastric injury macroscopically and microscopically. Moreover, FA displayed a marked decrease in the gastric levels of MDA, MPO, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and NF-κB p65 and a significant increase in SOD and GSH compared to the INDO group. Ultimately, 250 mg/kg FA was determined as the most effective dose. (4) Conclusion: Our results revealed that FA has a gastroprotective effect against indomethacin-induced gastric ulcers in rats due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. As a result, FA may be a potential treatment choice for gastric ulcers.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; ferulic acid; gastric ulcer; indomethacin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tkacs N., Herrmann L., Johnson R. Advanced Physiology and Pathophysiology: Essentials for Clinical Practice. Springer Publishing Company; New York, NY, USA: 2020.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

