Physiological and Anatomical Responses of Faba Bean Plants Infected with Chocolate Spot Disease to Chemical Inducers
- PMID: 36836749
- PMCID: PMC9963110
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020392
Physiological and Anatomical Responses of Faba Bean Plants Infected with Chocolate Spot Disease to Chemical Inducers
Abstract
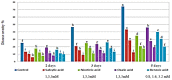
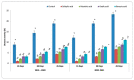
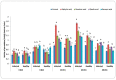
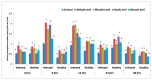
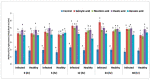
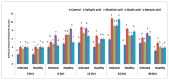
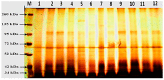
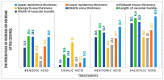
Plant diseases are biotic stresses that restrict crop plants' ability to develop and produce. Numerous foliar diseases, such as chocolate spots, can cause significant production losses in Vicia faba plants. Certain chemical inducers, including salicylic acid (SA), oxalic acid (OA), nicotinic acid (NA), and benzoic acid (BA), were used in this study to assess efficacy in controlling these diseases. A foliar spray of these phenolic acids was used to manage the impacts of the biotic stress resulting from disease incidence. All tested chemical inducers resulted in a significant decrease in disease severity. They also enhanced the defense system of treated plants through increasing antioxidant enzyme activity (Peroxidase, polyphenol oxidase, β-1, 3-glucanase, and chitinase) compared to the corresponding control. Healthy leaves of faba plants recorded the lowest (p < 0.05) values of all antioxidant activities compared to those plants infected by Botrytis fabae. Moreover, the separation of proteins using SDS-PAGE showed slight differences among treatments. Furthermore, foliar spray with natural organic acids reduced the adverse effects of fungal infection by expediting recovery. The SA (5 mM) treatment produced a pronounced increase in the upper, lower epidermis, palisade thickness, spongy tissues, midrib zone, length, and width of vascular bundle. The foliar application with other treatments resulted in a slight increase in the thickness of the examined layers, especially by benzoic acid. In general, all tested chemical inducers could alleviate the adverse effects of the biotic stress on faba bean plants infected by Botrytis fabae.
Keywords: Botrytis fabae; antioxidant enzymes; chocolate spot disease; faba bean; protein banding and anatomy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative Analysis of Defense Responses in Chocolate Spot-Resistant and -Susceptible Faba Bean (Vicia faba) Cultivars Following Infection by the Necrotrophic Fungus Botrytis fabae.Plant Pathol J. 2014 Dec;30(4):355-66. doi: 10.5423/PPJ.OA.06.2014.0050. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Plant Pathol J. 2014. PMID: 25506300 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Growth Morphology and Pathology, and Draft Genome Sequencing of Botrytis fabae, the Causal Organism of Chocolate Spot of Faba Bean (Vicia faba L.).Front Microbiol. 2020 Feb 18;11:217. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00217. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32132988 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing systemic resistance in faba bean (Vicia faba L.) to Bean yellow mosaic virus via soil application and foliar spray of nitrogen-fixing Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae strain 33504-Alex1.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Aug 2;13:933498. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.933498. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35982695 Free PMC article.
-
Conventional and Molecular Breeding Tools for Accelerating Genetic Gain in Faba Bean (Vicia Faba L.).Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 13;12:744259. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.744259. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34721470 Free PMC article.
-
Faba Bean Cultivation - Revealing Novel Managing Practices for More Sustainable and Competitive European Cropping Systems.Front Plant Sci. 2018 Aug 2;9:1115. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.01115. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 30116251 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amelioration of NaCl stress on germination, growth, and nitrogen fixation of Vicia faba at isosmotic Na-Ca combinations and Rhizobium.Planta. 2024 Feb 10;259(3):69. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04343-z. Planta. 2024. PMID: 38340188 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing agronomic performance, chocolate spot resistance, and heat tolerance for diverse Vicia faba genotypes under varying environmental conditions.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 22;14(1):9224. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59079-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38649406 Free PMC article.
-
Genome editing of the susceptibility gene ZmNANMT confers multiple disease resistance without agronomic penalty in maize.Plant Biotechnol J. 2023 Aug;21(8):1525-1527. doi: 10.1111/pbi.14078. Epub 2023 May 30. Plant Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37254611 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Protective Activity of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae Strain 33504-Mat209 against Alfalfa Mosaic Virus Infection in Faba Bean Plants.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jul 16;12(14):2658. doi: 10.3390/plants12142658. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crépon K., Marget P., Peyronnet C., Carrouée B., Arese P., Duc G. Nutritional value of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) seeds for feed and food. Field Crop. Res. 2010;115:329–339. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2009.09.016. - DOI
-
- Hassanein R.A., Hashem H.A., Khalil R.R. Stigmasterol treatment increases salt stress tolerance of faba bean plants by enhancing antioxidant systems. Plant Omics J. 2012;5:476–485.
-
- Hungria M., Vargas M.A. Environmental factors affecting nitrogen fixation in grain legumes in the tropics, with an emphasis on Brazil. Field Crop. Res. 2000;65:151–164. doi: 10.1016/S0378-4290(99)00084-2. - DOI
-
- Rhaïem Z., Cherif M., Kharrat M., Mejda Cherif M., Moncef Harrabi M. New faba bean genotypes resistant to chocolate spot caused by Botrytis fabae. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2002;41:99–108.
-
- El-Banoby F.E., Abd-AllA M.A., Tolba I.H., Morsy A.A., El-Gamal N.G., Khalil M.S.A. Biological control of chocolate spot disease of faba bean using some bioagents under field conditions. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2013;9:4021–4029.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

