Serum OPG and RANKL Levels as Risk Factors for the Development of Cardiovascular Calcifications in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients in Hemodialysis
- PMID: 36836810
- PMCID: PMC9967106
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020454
Serum OPG and RANKL Levels as Risk Factors for the Development of Cardiovascular Calcifications in End-Stage Renal Disease Patients in Hemodialysis
Abstract
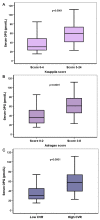
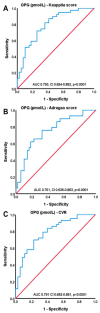
Cardiovascular calcifications (CVC) are frequently observed in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients and contribute to their cardiovascular mortality. The aim of the present study was to investigate the impact of osteoprotegerin (OPG)/Receptor Activator of NF-κΒ (RANK)/RANK ligand (RANKL) pathway in the development and evolution of CVCs in hemodialysis patients. In total, 80 hemodialysis patients were assessed for the presence of vascular (abdominal aorta and muscular arteries) calcifications and results were correlated to serum OPG and RANKL levels and the OPG/RANKL ratio. Traditional cardiovascular risk factors and mineral bone disease parameters were also estimated. The presence of VCs was also evaluated 5 years after the initiation of the study, and results were correlated to the initial serum OPG levels. Age, diabetes mellitus, coronary artery disease and OPG levels (p < 0.001) were associated with VCs, whereas RANKL levels were not. Multivariate analysis though revealed that only OPG levels were significantly associated with abdominal aorta calcifications (p = 0.026), but they were not correlated with the progression of VCs. Serum OPG levels are positively and independently associated with VCs in HD patients, but not with their progression. RANKL levels did not show any associations, whereas further studies are needed to establish the significance of OPG/RANKL ratio.
Keywords: RANKL; cardiovascular calcifications; chronic kidney disease; hemodialysis; osteoprotegerin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

