Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Rutin: Evaluation of Kinetic Parameters and Anti-Proliferative, Mutagenic and Anti-Mutagenic Effects
- PMID: 36836907
- PMCID: PMC9967632
- DOI: 10.3390/life13020549
Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Rutin: Evaluation of Kinetic Parameters and Anti-Proliferative, Mutagenic and Anti-Mutagenic Effects
Abstract
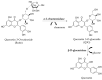
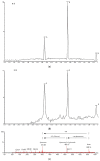
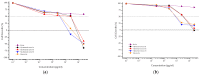
The bioavailability of glucoside flavonoids is influenced by the nature of the sugar, glucosides being absorbed faster than rhamnoglucosides, for example. One strategy to enhance the bioavailability is enzymatic hydrolysis. In this study, some kinetic parameters of hesperidinase-mediated hydrolysis of rutin were evaluated using an UHPLC/QTOF-MSE analysis of the products of a bioconversion reaction. The resulting hydrolyzed rutins (after 4, 8 and 12 h of reaction) were submitted to anti-proliferative and Cytokinesis-Block Micronucleus (CBMN) assays in CHO-K1 cells. In the hesperidinase-mediated hydrolysis, the final concentration of quercetin-3-O-glucoside (Q3G) was directly proportional to the rutin concentration and inversely proportional to the reaction time. At an anti-proliferative concentration (2.5 μg/mL), hydrolyzed rutin derivatives did not show a mutagenic effect, except for the sample with a higher content of Q3G (after 4 h of the enzymatic hydrolysis of rutin). Moreover, the higher Q3G content in hydrolyzed rutin protected the CHO-K1 cells 92% of the time against methyl methanesulfonate-induced mutagenic damage. These results suggested that the anti-mutagenic effect of hydrolyzed rutin might be related to antioxidant and cell death induction. Presenting a good lipophilicity/hydrophilicity ratio, together with antioxidant and anti-mutagenic activities, the hesperidinase-mediated hydrolyzed rutin seemed to be a promisor raw material for the development of food supplements.
Keywords: genotoxicity test; hesperidinase; quercetin-3-O-glucoside.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enzymatically modified isoquercitrin, alpha-oligoglucosyl quercetin 3-O-glucoside, is absorbed more easily than other quercetin glycosides or aglycone after oral administration in rats.Biol Pharm Bull. 2009 Dec;32(12):2034-40. doi: 10.1248/bpb.32.2034. Biol Pharm Bull. 2009. PMID: 19952424
-
Enzymatic de-glycosylation of rutin improves its antioxidant and antiproliferative activities.Food Chem. 2013 Nov 1;141(1):266-73. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.02.127. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Food Chem. 2013. PMID: 23768357
-
Transformation of rutin to antiproliferative quercetin-3-glucoside by Aspergillus niger.J Agric Food Chem. 2010 Oct 27;58(20):10886-92. doi: 10.1021/jf102871g. Epub 2010 Oct 1. J Agric Food Chem. 2010. PMID: 20886886
-
Chemical characterisation and toxicity assessment in vitro and in vivo of the hydroethanolic extract of Terminalia argentea Mart. leaves.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Dec 5;227:56-68. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.08.025. Epub 2018 Aug 22. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30142424
-
[Enzymatic synthesis of acylated quercetin 3-O-glycosides: a review].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2021 Jun 25;37(6):1900-1918. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.200769. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34227284 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Phenological Variations in the Content of Polyphenols and Triterpenoids in Epilobium angustifolium Herb Originating from Ukraine.Plants (Basel). 2023 Dec 31;13(1):120. doi: 10.3390/plants13010120. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38202428 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of Nrf2 and FXR via Natural Compounds in Liver Inflammatory Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 18;25(20):11213. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011213. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seasonal Chemical Variability and Antimicrobial, Anti-Proliferative Potential of Essential Oils from Baccharis uncinella, B. retusa, and B. calvescens (Asteraceae).Plants (Basel). 2025 Apr 26;14(9):1311. doi: 10.3390/plants14091311. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40364340 Free PMC article.
-
Highly Sensitive and Selective Fluorescence and Smartphone-Based Sensor for Detection of Rutin Using Boron Nitrogen Co-doped Graphene Quantum Dots.J Fluoresc. 2025 Jun;35(6):4321-4333. doi: 10.1007/s10895-024-03823-5. Epub 2024 Jul 12. J Fluoresc. 2025. PMID: 38995477
-
Sambucus nigra-Lyophilized Fruit Extract Attenuated Acute Redox-Homeostatic Imbalance via Mutagenic and Oxidative Stress Modulation in Mice Model on Gentamicin-Induced Nephrotoxicity.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 13;18(1):85. doi: 10.3390/ph18010085. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861148 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Izquierdo-Vega J.A., Morales-González J.A., SánchezGutiérrez M., Betanzos-Cabrera G., Sosa-Delgado S.M., Sumaya-Martínez M.T., Morales-González Á., Paniagua-Pérez R., Madrigal-Bujaidar E., Madrigal-Santillán E. Evidence of some natural products with antigenotoxic effects. Part 1: Fruits and polysaccharides. Nutrients. 2017;9:102. doi: 10.3390/nu9020102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- López-Romero D., Izquierdo-Vega J.A., Morales-González J.A., Madrigal-Bujaidar E., Chamorro-Cevallos G., Sánchez-Gutiérrez M., Betanzos-Cabrera G., Alvarez-Gonzalez I., Morales-González Á., Madrigal-Santillán E. Evidence of some natural products with antigenotoxic effects. Part 2: Plants, vegetables, and natural resin. Nutrients. 2018;10:1954. doi: 10.3390/nu10121954. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

