3D DEM Simulations and Experiments on Spherical Impactor Penetrating into the Elongated Particles
- PMID: 36837294
- PMCID: PMC9963823
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16041664
3D DEM Simulations and Experiments on Spherical Impactor Penetrating into the Elongated Particles
Abstract
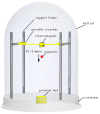
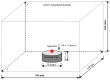
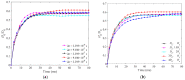
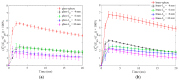
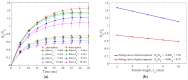
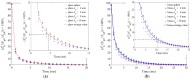
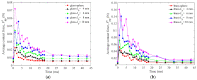
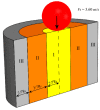
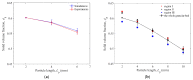
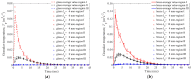
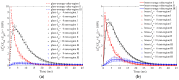
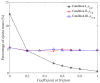
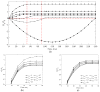
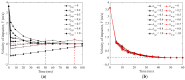
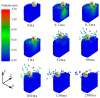
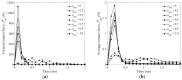
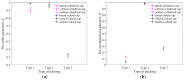
In this study, a brass or glass spherical impactor vertically penetrating into a granular bed composed of mono-sized spherical or elongated particles was simulated with three-dimensional (3D) discrete element method (DEM). Good agreement of the particle masses in the cup before and after penetration can be found in the simulations and experiments. The effects of particle length (Lp), friction coefficient, and particle configuration on the penetration depth of the impactor, ejecta mass, and solid volume fraction describing the response of the granular bed are discussed. The penetration depth is negatively correlated with Lp as the corresponding solid volume fraction of the granular bed decreases. A smaller friction coefficient leads to a larger penetration depth of the impactor and more ejection of particles. When the impactor is penetrating the Lp = 10 mm elongated particles, the penetration depth is negatively correlated to the order parameter and solid volume fraction.
Keywords: discrete element method; elongated particles; impact experiment; impaction; particle orientation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Bötschi S., Rajagopalan A.K., Rombaut I., Morari M., Mazzotti M. From needle-like toward equant particles: A controlled crystal shape engineering pathway. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2019;131:106581. doi: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2019.106581. - DOI
-
- Guidelli E.J., Ramos A.P., Zaniquelli M.E.D., Nicolucci P., Baffa O. Synthesis and characterization of silver/alanine nanocomposites for radiation detection in medical applications: The influence of particle size on the detection properties. Nanoscale. 2012;4:2884. doi: 10.1039/c2nr30090g. - DOI - PubMed

