Salubrinal Ameliorates Inflammation and Neovascularization via the Caspase 3/Enos Signaling in an Alkaline-Induced Rat Corneal Neovascularization Model
- PMID: 36837524
- PMCID: PMC9961429
- DOI: 10.3390/medicina59020323
Salubrinal Ameliorates Inflammation and Neovascularization via the Caspase 3/Enos Signaling in an Alkaline-Induced Rat Corneal Neovascularization Model
Abstract
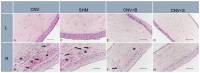
Background and Objectives: Ocular alkaline burn is a clinical emergency that can cause permanent vision loss due to limbal stem cell deficiency and corneal neovascularization (CNV). Although the basic pathogenetic mechanisms are considered to be acute oxidative stress and corneal neovascularization triggered by inflammation, the underlying intracellular mechanisms have not been clearly elucidated. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress on inflammation and neovascularization, and the effect of the ER stress inhibitor salubrinal (SLB), as a novel treatment in a corneal alkaline burn model in rats. Methods: Chemical burns were created by cautery for 4 s using a rod coated with 75% silver nitrate and 25% potassium nitrate in the corneal center for the corneal neovascularization (CNV) model. Twenty-eight Wistar albino rats were divided into four groups: SHAM, CNV, CNV + SLB, and CNV + bevacizumab (BVC). After the CNV model was applied to the right eye, a single subconjunctival dose (0.05 mL) of 1 mg/kg salubrinal was injected into both eyes in the CNV + SLB group. A total of 1.25 mg/mL of subconjunctival BVC was administered to the CNV + BVC group. Fourteen days after experimental modeling and drug administration, half of the globes were placed in liquid nitrogen and stored at -20 °C until biochemical analysis. The remaining tissues were collected and fixed in 10% buffered formalin for histopathological and immunohistochemical analysis. Three qualitative agents from three different pathways were chosen: TNFR for inflammation, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (e-NOS) for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-mediated vascular permeability, and caspase-3 for cellular apoptosis. Results: Significantly lower caspase-3 and eNOS levels were detected in the CNV + SLB and CNV + BVC groups than in the CNV group. Additionally, histopathological evaluation revealed a significant decrease in neovascularization, inflammatory cell infiltration, and fibroblast activity in the CNV + SLB and CNV + BVC groups. The endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibitor, salubrinal, administered to the treatment group, attenuated apoptosis (caspase-3) and inflammation (e-NOS). In the control group (left eyes of the SLB group), salubrinal did not have a toxic effect on the healthy corneas. Conclusion: The ER stress pathway plays an important role in angiogenesis after alkaline corneal burns, and treatment with SLB modulates this pathway, reducing caspase-3 and eNOS levels. Further studies are needed to understand the molecular mechanisms altered by SLB-mediated therapy. The fact that more than one mechanism plays a role in the pathogenesis of CNV may require the use of more than one molecule in treatment. SLB has the potential to affect multiple steps in CNV pathogenesis, both in terms of reducing ER stress and regulating cellular homeostasis by inhibiting the core event of integrated stress response (ISR). Therefore, it can be used as a new treatment option and as a strengthening agent for existing treatments. Although blockade of intracellular organelle stress pathways has shown promising results in experimental studies, more in-depth research is needed before it can be used in routine practice. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to report the role of ER stress in corneal injury.
Keywords: apoptosis; corneal injury; eNOS; endoplasmic reticulum stress; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of Dexpanthenol on Corneal Neovascularization and Inflammation on Rat Model.Cornea. 2025 Jan 14;44(7):905-910. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000003804. Cornea. 2025. PMID: 39808129
-
Comparison of the Effects of Dovitinib and Bevacizumab on Reducing Neovascularization in an Experimental Rat Corneal Neovascularization Model.Cornea. 2019 Sep;38(9):1161-1168. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000002012. Cornea. 2019. PMID: 31180924
-
The impact of subconjuctivally injected EGF and VEGF inhibitors on experimental corneal neovascularization in rat model.Curr Eye Res. 2011 Nov;36(11):1005-13. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2011.601840. Curr Eye Res. 2011. PMID: 21999227
-
Effect of topical motesanib in experimental corneal neovascularization model.Int Ophthalmol. 2023 Aug;43(8):2989-2997. doi: 10.1007/s10792-023-02685-3. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Int Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36971928 Review.
-
Role of macrophage in ocular neovascularization.Heliyon. 2024 May 7;10(10):e30840. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30840. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38770313 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a novel targeted approach to repair bone defects by regulating osteogenesis and angiogenesis.J Transl Med. 2023 Jul 18;21(1):480. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04328-8. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37464413 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of SLIT3-ROBO4 Signaling in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Delayed Corneal Epithelial and Nerve Regeneration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 May 1;65(5):8. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.5.8. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38700874 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative study on corneal epithelium healing: effects of crosslinked hyaluronic acid and amniotic membrane extract eye drops in rats.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Jul 24;11:1415658. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1415658. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39113726 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation in cornea and corneal diseases: a systematic review.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Apr 8;10(1):169. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-01935-2. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 38589350 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kubota M., Shimmura S., Kubota S., Miyashita H., Kato N., Noda K., Ozawa Y., Usui T., Ishida S., Umezawa K., et al. Hydrogen andN-Acetyl-l-Cysteine Rescue Oxidative Stress-Induced Angiogenesis in a Mouse Corneal Alkali-Burn Model. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011;52:427–433. doi: 10.1167/iovs.10-6167. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang H., Wang Z.-W., Wu H.-B., Li Z., Li L.-C., Hu X.-P., Ren Z.-L., Li B.-J., Hu Z. Transforming growth factor-β1 induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in rat vascular smooth muscle cells via ROS-dependent ERK–NF-κB pathways. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2013;375:11–21. doi: 10.1007/s11010-012-1512-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

