Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Membranes for Vascular Stent Coating: Manufacturing, Biomedical and Surgical Applications, Innovations and Case Reports
- PMID: 36837743
- PMCID: PMC9967047
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes13020240
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Membranes for Vascular Stent Coating: Manufacturing, Biomedical and Surgical Applications, Innovations and Case Reports
Abstract
Coated stents are defined as innovative stents surrounded by a thin polymer membrane based on polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)useful in the treatment of numerous vascular pathologies. Endovascular methodology involves the use of such devices to restore blood flow in small-, medium- and large-calibre arteries, both centrally and peripherally. These membranes cross the stent struts and act as a physical barrier to block the growth of intimal tissue in the lumen, preventing so-called intimal hyperplasia and late stent thrombosis. PTFE for vascular applications is known as expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (e-PTFE) and it can be rolled up to form a thin multilayer membrane expandable by 4 to 5 times its original diameter. This membrane plays an important role in initiating the restenotic process because wrapped graft stent could be used as the treatment option for trauma devices during emergency situations and to treat a number of pathological vascular disease. In this review, we will investigate the multidisciplinary techniques used for the production of e-PTFE membranes, the advantages and disadvantages of their use, the innovations and the results in biomedical and surgery field when used to cover graft stents.
Keywords: PTFE; covered stent; membrane; vascular disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
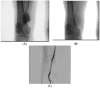
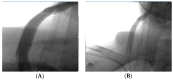
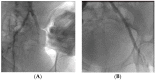
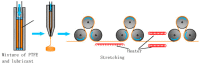
References
-
- Roina Y., Auber F., Hocquet D., Herlem G. ePTFE functionalization for medical applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2021;20:100412. doi: 10.1016/j.mtchem.2020.100412. - DOI
-
- Aronson J.K., editor. Meyler’s Side Effects of Drugs. 16th ed. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2016. Polytetrafluoroethylene; pp. 872–873.
-
- Huang H., Yao Q., Zhang X., Wang H. Microporous expanded polytetrafluoroethylene layer functionalized hydrophilic groups for excellent mechanical durability and superior performance in proton exchange membrane fuel cell. J. Power Sources. 2022;526:231130. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.231130. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

