Application Prospects of MXenes Materials Modifications for Sensors
- PMID: 36837947
- PMCID: PMC9959414
- DOI: 10.3390/mi14020247
Application Prospects of MXenes Materials Modifications for Sensors
Abstract
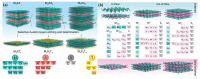
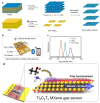
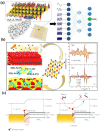
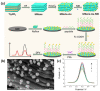
The first two-dimensional (2D) substance sparked a boom in research since this type of material showed potential promise for applications in field sensors. A class of 2D transition metal nitrides, carbides, and carbonitrides are referred to as MXenes. Following the 2011 synthesis of Ti3C2 from Ti3AlC2, much research has been published. Since these materials have several advantages over conventional 2D materials, they have been extensively researched, synthesized, and studied by many research organizations. To give readers a general understanding of these well-liked materials, this review examines the structures of MXenes, discusses various synthesis procedures, and analyzes physicochemistry properties, particularly optical, electronic, structural, and mechanical properties. The focus of this review is the analysis of modern advancements in the development of MXene-based sensors, including electrochemical sensors, gas sensors, biosensors, optical sensors, and wearable sensors. Finally, the opportunities and challenges for further study on the creation of MXenes-based sensors are discussed.
Keywords: MXenes nanomaterial; biosensor; electrochemistry sensor; gas sensor; optical sensor; wearable sensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




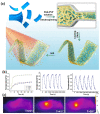
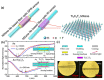
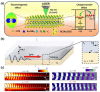

References
-
- Grabowski K., Srivatsa S., Vashisth A., Mishnaevsky L., Uhl T. Recent advances in MXene-based sensors for Structural Health Monitoring applications: A review. Measurement. 2022;189:110575. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.110575. - DOI
-
- Tran A.V., Shim K., Vo Thi T.T., Kook J.K., An S.S.A., Lee S.W. Targeted and controlled drug delivery by multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles with internal fluorescent conjugates and external polydopamine and graphene oxide layers. Acta Biomater. 2018;74:397–413. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.05.022. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

