Antibiotic Susceptibility and Molecular Typing of Invasive Haemophilus influenzae Isolates, with Emergence of Ciprofloxacin Resistance, 2017-2021, Italy
- PMID: 36838281
- PMCID: PMC9965257
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11020315
Antibiotic Susceptibility and Molecular Typing of Invasive Haemophilus influenzae Isolates, with Emergence of Ciprofloxacin Resistance, 2017-2021, Italy
Abstract
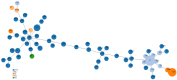
Haemophilus influenzae invasive disease is a severe infection that needs rapid antibiotic therapy. The aim of the study was to perform and evaluate the serotype distribution, antibiotic susceptibility and molecular characteristics of 392 H. influenzae invasive isolates collected during 2017-2021 in Italy. The majority of isolates were NTHi (305/392, 77.8%), followed by Hib (49/392, 12.5%). Ampicillin resistance was frequently detected (85/392, 21.7%): 12.2% were β-lactamase producers (all blaTEM except one blaROB), 9.4% were β-lactamase-negative ampicillin-resistant (BLNAR), with mutations in the ftsI gene. Six isolates were resistant to ciprofloxacin, with substitutions in GyrA and ParC. An MLST analysis revealed the occurrence of international resistant clones, such as ST103 and ST14, highlighting the importance of molecular surveillance.
Keywords: Haemophilus influenzae; MLST; antibiotic resistance; quinolone resistance; surveillance; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Peltola H. Worldwide Haemophilus influenzae type b disease at the beginning of the 21st century: Global analysis of the disease burden 25 years after the use of the polysaccharide vaccine and a decade after the advent of conjugates. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000;13:302–317. doi: 10.1128/CMR.13.2.302. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) Haemophilus influenzae Annual Epidemiological Report for 2018. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC); Stockholm, Sweden: 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

