Mechanisms and Applications of Bacterial Inoculants in Plant Drought Stress Tolerance
- PMID: 36838467
- PMCID: PMC9958599
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11020502
Mechanisms and Applications of Bacterial Inoculants in Plant Drought Stress Tolerance
Abstract
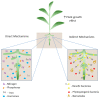
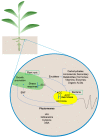
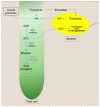
Agricultural systems are highly affected by climatic factors such as temperature, rain, humidity, wind, and solar radiation, so the climate and its changes are major risk factors for agricultural activities. A small portion of the agricultural areas of Brazil is irrigated, while the vast majority directly depends on the natural variations of the rains. The increase in temperatures due to climate change will lead to increased water consumption by farmers and a reduction in water availability, putting production capacity at risk. Drought is a limiting environmental factor for plant growth and one of the natural phenomena that most affects agricultural productivity. The response of plants to water stress is complex and involves coordination between gene expression and its integration with hormones. Studies suggest that bacteria have mechanisms to mitigate the effects of water stress and promote more significant growth in these plant species. The underlined mechanism involves root-to-shoot phenotypic changes in growth rate, architecture, hydraulic conductivity, water conservation, plant cell protection, and damage restoration through integrating phytohormones modulation, stress-induced enzymatic apparatus, and metabolites. Thus, this review aims to demonstrate how plant growth-promoting bacteria could mitigate negative responses in plants exposed to water stress and provide examples of technological conversion applied to agroecosystems.
Keywords: PGPB; abiotic stress; bioinoculant; endophytic bacteria; sustainable agriculture; water-use efficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimistic contributions of plant growth-promoting bacteria for sustainable agriculture and climate stress alleviation.Environ Res. 2023 Jan 15;217:114924. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.114924. Epub 2022 Nov 26. Environ Res. 2023. PMID: 36471556 Review.
-
Drought tolerance improvement in plants: an endophytic bacterial approach.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Sep;103(18):7385-7397. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10045-4. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31375881 Review.
-
Enhancement of Plant Productivity in the Post-Genomics Era.Curr Genomics. 2016 Aug;17(4):295-6. doi: 10.2174/138920291704160607182507. Curr Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27499678 Free PMC article.
-
Plant survival under drought stress: Implications, adaptive responses, and integrated rhizosphere management strategy for stress mitigation.Microbiol Res. 2021 Jan;242:126626. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2020.126626. Epub 2020 Oct 18. Microbiol Res. 2021. PMID: 33189069 Review.
-
Advances in Wheat Physiology in Response to Drought and the Role of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria to Trigger Drought Tolerance.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 26;9(4):687. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040687. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33810405 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Juvenile Plant-Microbe Interactions Modulate the Adaptation and Response of Forest Seedlings to Rapid Climate Change.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 9;13(2):175. doi: 10.3390/plants13020175. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256729 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design of Microbial Consortia Based on Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi, Yeasts, and Bacteria to Improve the Biochemical, Nutritional, and Physiological Status of Strawberry Plants Growing under Water Deficits.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 4;13(11):1556. doi: 10.3390/plants13111556. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38891364 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Role of Streptomyces Composite Inoculants in Mitigating Wheat Drought Stress Under Field Conditions.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 25;14(3):366. doi: 10.3390/plants14030366. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39942929 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effect of Serratia fonticola and Pseudomonas koreensis on Mitigating Salt Stress in Cucumis sativus L.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Mar 15;47(3):194. doi: 10.3390/cimb47030194. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40136448 Free PMC article.
-
Boosting drought resilience: the role of endophytic Bacillus safensis in enhancing melatonin production in chickpea cultivars.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):789. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06830-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40597616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Malhi G.S., Kaur M., Kaushik P. Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture and Its Mitigation Strategies: A Review. Sustainability. 2021;13:1318. doi: 10.3390/su13031318. - DOI
-
- Rao D.E., Chaitanya K.V. Photosynthesis and antioxidative defense mechanisms in deciphering drought stress tolerance of crop plants. Biol. Plant. 2016;60:201–218. doi: 10.1007/s10535-016-0584-8. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
- E-26/203.003/2017, E-26/201.142/2021 and E-26/211.223/2021/Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro
- n°88882.632756/2021-01 and 88887.676823/2022-00/Coordenação de Aperfeicoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior
- 314.263/2018-7/National Council for Scientific and Technological Development
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

