Bioremediation of Oil-Contaminated Soil of the Republic of Kazakhstan Using a New Biopreparation
- PMID: 36838488
- PMCID: PMC9960684
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11020522
Bioremediation of Oil-Contaminated Soil of the Republic of Kazakhstan Using a New Biopreparation
Abstract
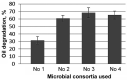
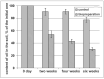
A new biopreparation is developed to clean soils from oil pollution in the arid climate of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The biopreparation includes bacterial strains R. qingshengii F2-1, R. qingshengii F2-2, and P. alloputida BS3701. When using the biopreparation in a liquid mineral medium with 15% crude oil, laboratory studies have revealed degradation of 48% n-alkanes and 39% of PAHs after 50 days. The effectiveness of the biopreparation has been demonstrated in field experiments in the soil contaminated with 10% crude oil at the K-Kurylys landfill, Republic of Kazakhstan. During the six-month field experiment, the number of oil degraders reached 107 CFU/g soil, which degraded 70% of crude oil by the end of the experiment.
Keywords: PAHs; alkanes; biodegradation; crude oil; field trials; microbial consortia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Crude Oil Biodegradation by Newly Isolated Bacterial Strains and Their Consortium Under Soil Microcosm Experiment.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019 Dec;189(4):1223-1244. doi: 10.1007/s12010-019-03058-2. Epub 2019 Jun 24. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31236896
-
Oil-Contaminated Soil Remediation with Biodegradation by Autochthonous Microorganisms and Phytoremediation by Maize (Zea mays).Molecules. 2023 Aug 17;28(16):6104. doi: 10.3390/molecules28166104. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37630356 Free PMC article.
-
Adsorptive bioremediation of soil highly contaminated with crude oil.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Mar 1;706:135739. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135739. Epub 2019 Nov 25. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 31818568
-
Rapid degradation of long-chain crude oil in soil by indigenous bacteria using fermented food waste supernatant.Waste Manag. 2019 Feb 15;85:361-373. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2018.12.041. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Waste Manag. 2019. PMID: 30803591
-
Degradation of n-alkanes and PAHs from the heavy crude oil using salt-tolerant bacterial consortia and analysis of their catabolic genes.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Apr;24(12):11392-11403. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-8446-2. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28315056
Cited by
-
Bioremediation of Automotive Residual Oil-Contaminated Soils by Biostimulation with Enzymes, Surfactant, and Vermicompost.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Aug 18;20(16):6600. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20166600. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37623183 Free PMC article.
-
Uncontrolled Post-Industrial Landfill-Source of Metals, Potential Toxic Compounds, Dust, and Pathogens in Environment-A Case Study.Molecules. 2024 Mar 27;29(7):1496. doi: 10.3390/molecules29071496. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38611776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kvenvolden K.A., Cooper C.K. Natural seepage of crude oil into the marine environment. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2003;23:140–146. doi: 10.1007/s00367-003-0135-0. - DOI
-
- Xu H.-L., Chen J.-N., Wang S.-D., Liu Y. Oil spill forecast model based on uncertainty analysis: A case study of Dalian Oil Spill. Ocean Eng. 2012;54:206–212. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2012.07.019. - DOI
-
- Glazovskaya M.A. Rehabilitation of Oil-Contaminated Soil Ecosystems. Nauka; Moscow, Russia: 1988. p. 254.
-
- Kaiser M.J., Pulsipher A.G. A review of the oil and gas sector in Kazakhstan. Energy Policy. 2007;35:1300–1314. doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2006.03.020. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

