Extraction Bottleneck in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2: Evaluation of an Alternative Protocol Derived from Veterinary Use
- PMID: 36838500
- PMCID: PMC9960603
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms11020535
Extraction Bottleneck in the Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2: Evaluation of an Alternative Protocol Derived from Veterinary Use
Abstract
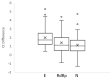
The COVID-19 pandemic represented a challenge for health-care systems, and a major bottleneck in SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis was the unavailability of extraction reagents. To overcome this limitation, we performed a comparative analysis to evaluate the performance of an alternative extraction protocol derived from veterinary use adapted to an open robotic platform (Testing method). A total of 73 nasopharyngeal swabs collected for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection were simultaneously extracted with the Testing protocol and the laboratory Standard of Care in order to assess the performance of the first one. The Cohen's coefficient between both procedures was excellent (K Value = 0.955). Analysis of cycle threshold and linear regression showed a significant correlation between the two methods for each tested genetic target. Although validated for veterinary applications, the Testing method showed excellent performances in RNA extraction, with several advantages: lower sample input volume, the possibility to overcome the lack of deep-well plates and adaptability to robotic liquid handlers.
Keywords: COVID-19; RNA; SARS-CoV-2; automated extraction; liquid handler.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High-Throughput COVID-19 Testing of Naso-Oropharyngeal Swabs Using a Sensitive Extraction-Free Sample Preparation Method.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0135822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01358-22. Epub 2022 Aug 11. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35950846 Free PMC article.
-
Automated SARS-COV-2 RNA extraction from patient nasopharyngeal samples using a modified DNA extraction kit for high throughput testing.Ann Saudi Med. 2020 Sep-Oct;40(5):373-381. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2020.373. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Ann Saudi Med. 2020. PMID: 32954791 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Evaluation of the cobas SARS-CoV-2 Test and a Diagnostic Platform Switch during 48 Hours in the Midst of the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Clin Microbiol. 2020 May 26;58(6):e00599-20. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00599-20. Print 2020 May 26. J Clin Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32277022 Free PMC article.
-
A Multiplex One-Step RT-qPCR Protocol to Detect SARS-CoV-2 in NP/OP Swabs and Saliva.Curr Protoc. 2021 May;1(5):e145. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.145. Curr Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34004070 Free PMC article.
-
[Evaluation of a Visually-Read Rapid Antigen Test Kit (SGA V-Chek) for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Virus].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2021 Jul;55(3):461-464. doi: 10.5578/mb.20219815. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2021. PMID: 34416811 Turkish.
Cited by
-
Clinical Evaluation and Comparison of Two Microfluidic Antigenic Assays for Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Virus.Microorganisms. 2023 Nov 5;11(11):2709. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11112709. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 38004721 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous